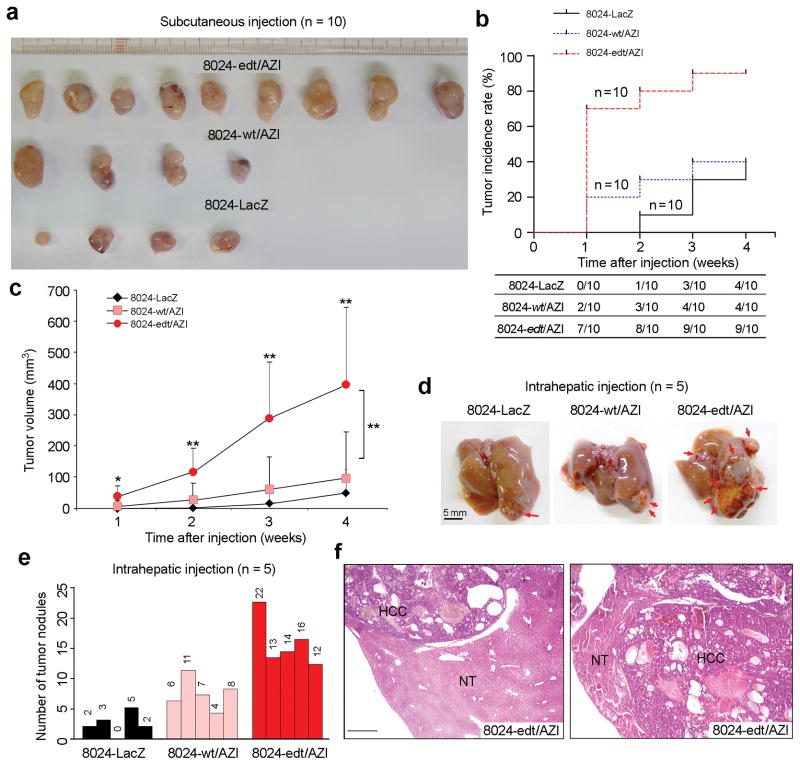
Figure 4.
AZIN1 editing contributes to augmented tumor initiating potential and enhanced in vivo tumorigenic ability. (a) Tumors derived from 8024-LacZ, 8024-wt/AZI and 8024-edt/AZI cells 4 weeks post subcutaneous injection (n = 10 per group). (b) Cumulative tumor incidence curves of severe combined immunodeficient (SCID) mice from the indicated cell lines estimated by the Kaplan-Meier method. (c) Growth curves of tumors derived from the indicated cell lines over a period of 4 weeks (*, P<0.05; **, P<0.01). Statistical significance was determined by unpaired, two-tailed Student’s t test. (d) Representative images of mouse livers that underwent intrahepatic inoculation with 8024-wt/AZI, 8024-edt/AZI and 8024-LacZ cells 4 weeks post-injection (n = 5). Arrows indicate focal tumor nodules on liver surfaces. Scale bar: 5 mm. (e) The numbers of tumor nodules (larger than 1 mm in diameter). (f) H&E staining showing severe HCC lesions in 8024-edt/AZI-injected livers. NT, adjacent non-tumor. Scale bar: 200 μm.