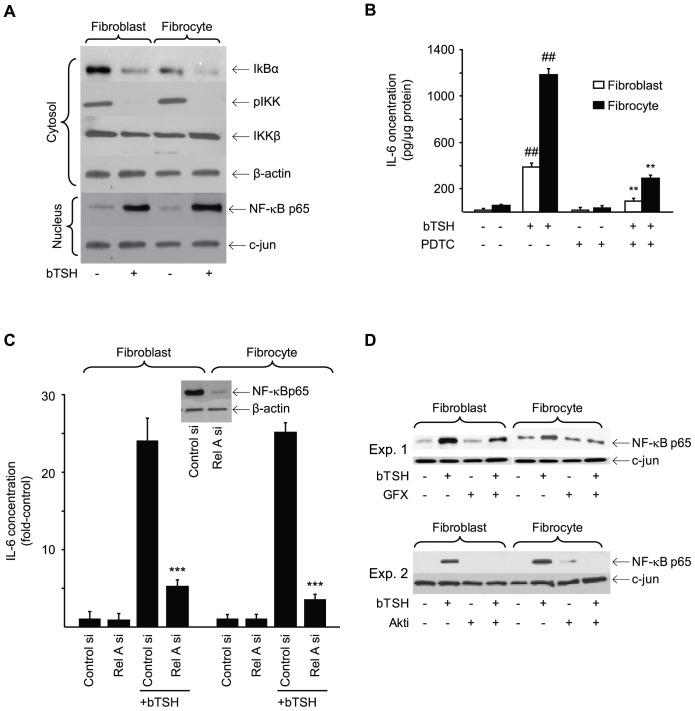
Figure 11. Involvement of NF-κB in the induction of IL-6 by bTSH.
(A) Confluent orbital fibroblast and fibrocyte cultures were treated without or with bTSH for 60 min. Cytosolic and nuclear protein fractions were prepared as described in Experimental Procedures. Nuclear protein extract was probed with anti-NF-κB-p65 Abs by Western blot analysis. Densitometry: nuclear p65, control vs bTSH-treated fibroblasts, 11.72 AU vs 58.5 AU; fibrocytes, 10.2 AU vs 75.3 AU, respectively. Cytosolic extracts were subjected to Western blot analysis of IκBα, pIKK, and IKKβ. (B) Orbital fibroblasts, in this case from a patient with TAO, and fibrocytes were treated with nothing or bTSH (5 mIU/mL) in the absence or presence of PDTC (100 µM) for 16 h. Media were analyzed for IL-6 content by ELISA. Data are presented as the mean ± SD of 3 independent determinations. (##, P<0.01 vs untreated controls; **, P<0.01 vs TSH alone). (C) Sub-confluent orbital fibroblast and fibrocyte cultures were transfected with control siRNA or that targeting Rel A, incubated for 48 h. and then treated with nothing or bTSH (5 mIU/mL) for 16 h. Media were analyzed for IL-6. Inset: Western blot confirming knockdown of Rel A. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD of three independent determinations. ***, p<0.001 vs control siRNA. (D) Orbital fibroblasts and fibrocytes were treated with nothing or bTSH (5 mIU/mL) in the absence or presence of GFX (10 µM) or Akti (1 µM) for 30 min. Nuclear protein fractions were prepared as described in Experimental Procedures and probed with anti-NF-κB-p65 Abs by Western blotting. Densitometry: Fibroblasts bTSH vs bTSH plus GFX, 0.826±0.196 AU vs 0.485±0.06 AU, bTSH vs bTSH plus AKTi, 0.253±0.02 AU vs 0.0 AU; Fibrocytes, 0.575±0.072 AU vs 0.391±0.056 AU and 0.485±0.03 AU vs 0.043±0.012 AU respectively. In 3 separate experiments, GFX reduced TSH-dependent p65 levels by 42±7% and 32±8% in fibroblasts and fibrocytes, respectively. AKTi reduced these levels by 91±1% in fibrocytes.