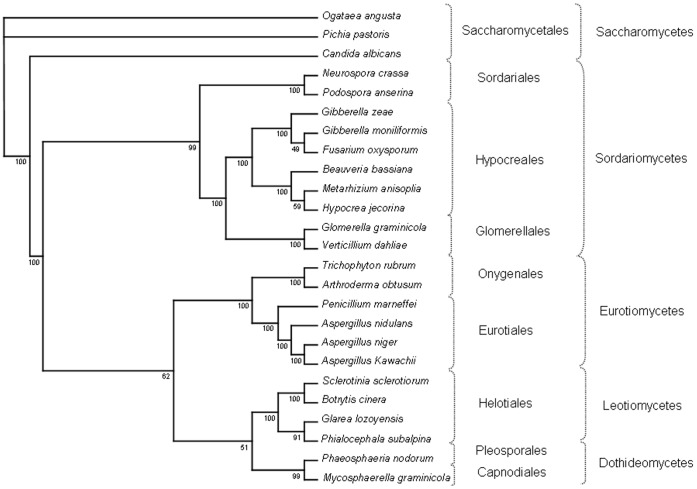
Figure 2. Phylogenetic analysis of G. lozoyensis based on mitochondrial protein sequences.
The evolutionary history was inferred by using the Maximum Likelihood method in PhyML 3.0 [38]. The tree was based on 12 OXPHOS proteins ATP6, COB, COX1, COX2, COX3, NAD1, NAD2, NAD3, NAD4, NAD4L, NAD5 and NAD6 from 25 fungi: G. zeae (NC_009493), G. moniliformis (NC_016687), F. oxysporum (NC_017930), H. jecorina (NC_NC003388), M. anisopliae (NC_008068), B. bassiana (NC_010652), G. graminicola (CM001021), V. dahliae (NC_008248), N. crassa (NC_001570), P. anserina (NC_001329), P. nodorum (NC_009746), M. graminicola (NC_010222), P. subalpina (NC_015789), T. rubrum (NC_012824), A. obtusum (NC_012830), P. marneffei (NC_005256), E. nidulans (NC_017896), A. niger (NC_007445), A. kawachi (AP012272), C. albicans (NC_002653), O. angusta (NC_014805), P. pastoris (NC_015384), S. sclerotiorum and B. cinera (http://www.broadinstitute.org/).