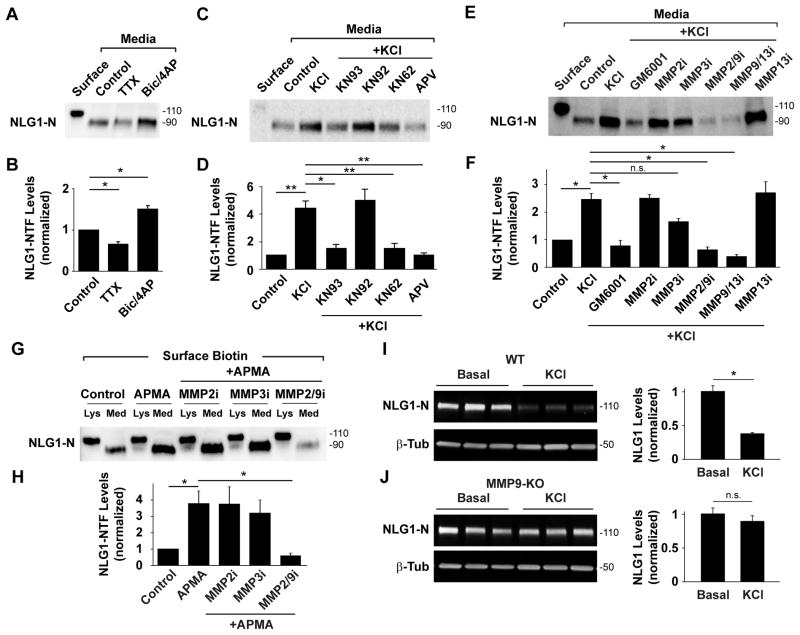
Figure 3. Neuronal Activity Induces NLG1 Cleavage Through NMDAR, CaMK, and MMP9 Signaling.
(A) Isolation and detection of NLG1-NTFs under control conditions or in the presence of TTX (2 μM) or bicuculline (50 μM) plus 4AP (25 μM, Bic/4AP). Surface- 10% of total surface protein at time zero.
(B) Means ± SEMs of NLG1-NTFs under indicated conditions normalized to control. n = 4, * p< 0.05.
(C) Isolation and detection of NLG1-NTFs under control conditions or in the presence of KCl (30 mM, 2 h) with or without indicated pharmacological agents.
(D) Means ± SEMs of NLG1-NTFs levels normalized to control. n = 4, * p< 0.05, ** p < 0.01.
(E) Isolation and detection of ~90 kDa NLG1-NTFs under control conditions or in the presence of KCl with or without MMP inhibitors. Note that inhibitors targeting MMP9 abrogate KCl-induced NLG1 cleavage.
(F) Means ± SEMs of NLG1-NTFs levels normalized to control. n = 8, *p < 0.005. n.s., not significant.
(G) Immunoblot analysis of NLG1 and NLG1-NTFs in biotinylated fractions of DIV21cortical neurons treated with the nonselective MMP activator APMA with or without MMP inhibitors. Lys- Whole lysates; Med- Media. Note that only 10% of precipitate was loaded in Lys lanes.
(H) Means ± SEMs of NLG1-NTFs produced under the indicated conditions normalized to control. n = 3, *p < 0.05.
(I–J) Immunoblot analysis of NLG1 in whole cell extracts from DIV18 cortical neuron cultures from (I) WT or (J) MMP9 KO mice following 2 h incubation in Neurobasal medium (Control) or medium with 30mM KCl (KCl). Bar graphs on the right represent means ± SEM of total NLG1 levels under the indicated conditions for WT (n = 6, *p < 0.01) and MMP9 KO neurons (n = 6, p > 0.05), respectively.