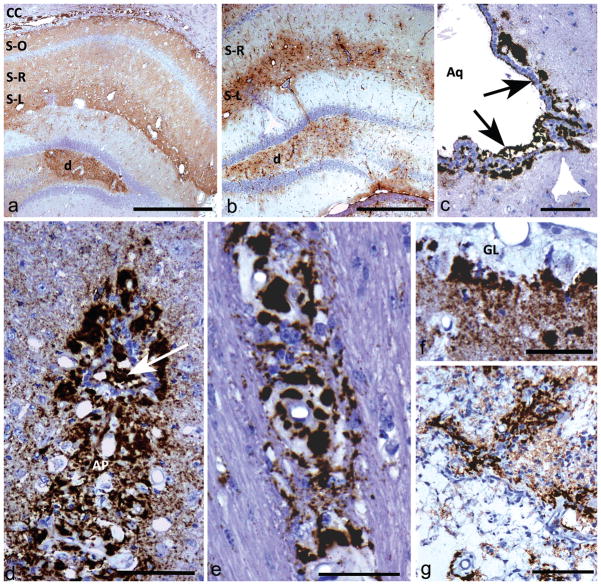
Fig 1. Light microscopic immunohistochemistry showing different types of PrPSSLOW labelling patterns and astrocytic gliosis.
a) Diffuse PrPSSLOW accumulation in hippocampus with increased intensity of labelling in the dentate gyrus (d), stratum lacunosum-moleculare (S-L) and in the corpus callosum (CC). S-R; stratum radiatum; S-O; stratum oriens.
b) GFAP immunolabelling showing gliosis predominantly in the dentate gyrus (d) and stratum lacunosum-moleculare (S-L). The stratum radiatum (S-R) of the hippocampus, which has mild-moderate punctuate PrPSSLOW labelling (see Fig 1a), does not show conspicuous astrocyte hypertrophy or hyperplasia.
c) PrPSSLOW accumulation within the ventricular space of the aqueduct of Sylvius (Aq); in the subjacent glial limitans and coating the ventricular surface of ependymal cells (arrows).
d) Marked PrPSSLOW accumulation within the area postrema (AP) and the central canal (arrow) at the level of the obex.
e) PrPSSLOW immunolabelling within the walls and surrounding blood vessels of the corpus callosum.
f) Marked thickening of the sub-pial glial limitans (GL) associated with marked PrPSSlow accumulation.
g) Marked PrPSSLOW accumulation associated with an old infarct.
a, c, e, f, g, h: PrPSSLOW immunolabelling; b, d: GFAP immunolabelling.
Mag bars: a = 500 μm, b = 500 μm, c =100 μm, d = 100 μm, e = 50 μm, f = 50 μm, g = 100 μm.