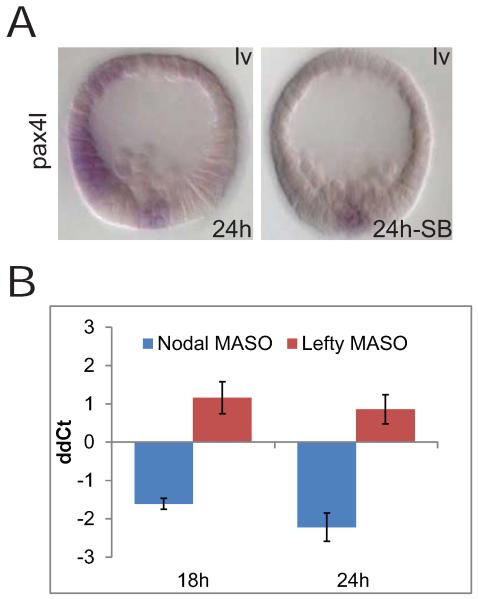
Figure 4.
pax4l is an oral ectodermal gene controlled by the nodal pathway. A) WMISH observations on pax4l. This experiment shows that ectodermal, but not mesodermal, expression of pax4l is completely lost if the Nodal signaling pathway is inhibited with SB-431542. The embryos were shown with the oral ectoderm facing left. B) Quantitative perturbation results. pax4l transcript levels are reduced in response to the nodal MASO, and increased by lefty MASO. Changes in expression levels of ectodermal genes were quantified by QPCR relative to poly-ubiquitin. Results shown as arithmetic mean ± standard deviation (ddCt:ΔΔCt, i.e., QPCR cycle number normalized to control Ct and to polyubiqitin Ct; 1 ddCt = 1.9 fold difference).