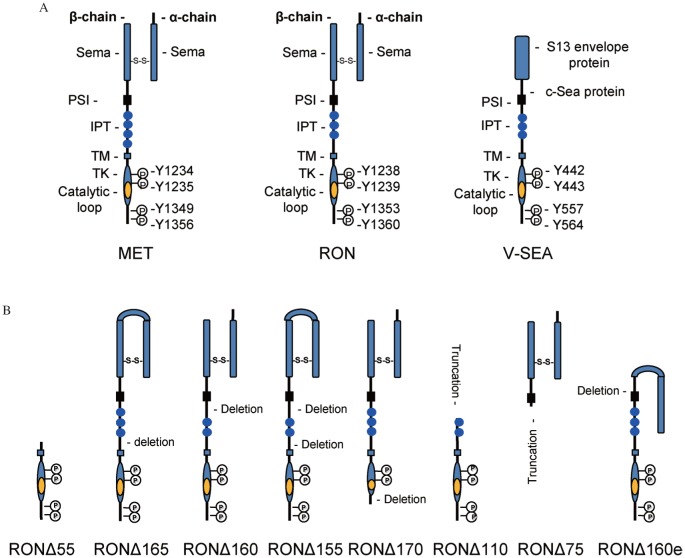
Fig. 1. Schematic representation of RON and RON variant.
A: General features of MET, RON, and V-SEA. MET is the classical example of this family. Mature RON consists of a 35 kDa α-chain and a 145 kDa β-chain linked by a disulfide bond. The α-chain resides extracellularly and contains a portion of Semaphorin (Sema). The β-chain comprises a large extracellular domain, a short transmembrane (TM) segment, and a cytoplasmic portion harboring a tyrosine kinase (TK) domain and a C-terminal tail. The Sema domain harbors a ligand-binding pocket for the MSP β-chain. Regulatory tyrosine residues Tyr1238 and Tyr1239 in the TK domain and Tyr1353 and Tyr1360 in the C-terminal tail are marked. V-SEA is an oncogenic protein fused by the avian S13 retroviral envelope protein with the chicken SEA sequences. PSI, Plexins-Semaphorins-Integrins; IPT, immunoglobulin-plexin-transcription. B: Different RON variants. RONΔ55 is derived from alternative initiation at Met913. RONΔ165 is formed by deletion of exon 11 coding 49 amino acids. RONΔ160 has a deletion of exons 5 and 6 coding 109 amino acids. RONΔ155 has a combined deletion of exons 5, 6 and 11. RONΔ170 is derived from deletion of exon 19 in the kinase domain. RONΔ110 is formed by N-terminal truncation at Arg631. RONΔ85 is a free variant with C-terminal truncation at Asp634 caused by insertion. RONΔ160e is derived by deletion of exon 2.