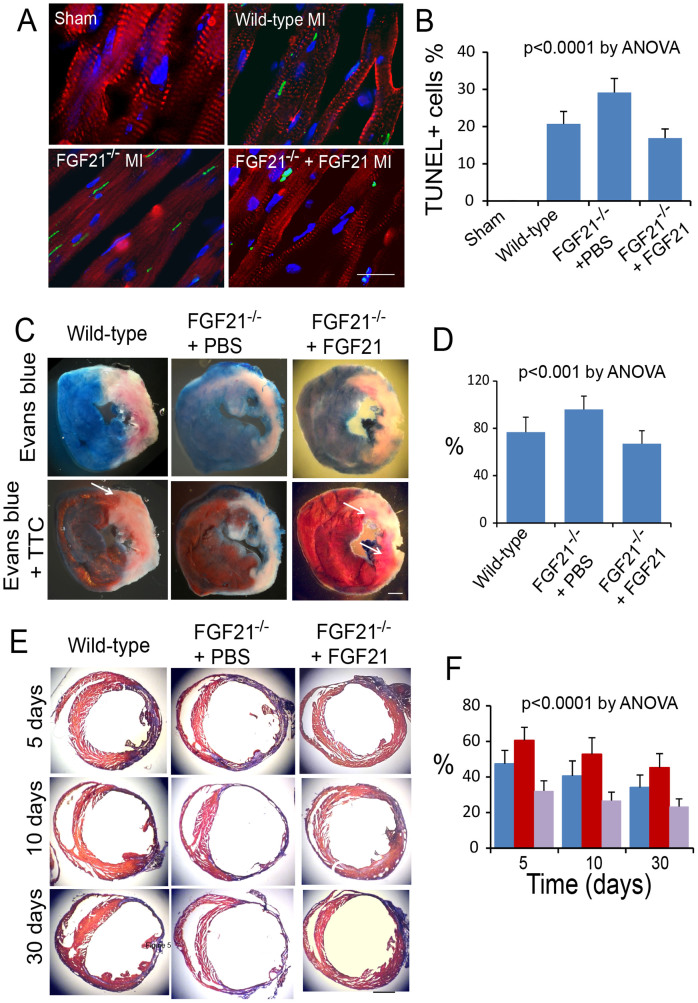
Figure 5. Cardioprotective action of FGF21 in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury.
(A) Immunofluorescence micrographs showing cells undergoing DNA fragmentation in the ischemic myocardium by the TUNEL assay. Red: Cardiac troponin I. Green: TUNEL-positive cell nuclei. Blue: Cell nuclei. Scale: 10 μm. (B) Graphic representation of the fraction of TUNEL-positive cell nuclei in the ischemic myocardium calculated in reference to the total cell nuclei. Means and SDs are presented (n = 8). The P value was estimated by ANOVA among all groups. The post-hoc pairwise multiple comparisons P values are presented in Supplementary Table 2. (C) Left ventricular slices from wild-type mice and FGF21−/− mice with administration of PBS or recombinant FGF21 at 24 hrs post myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury, showing the influence of FGF21 on the fraction of acute myocardial infarcts (by the TTC assay) in reference to the area at risk (by the Evans blue assay). Note that the left ventricular wall thickness is thinner in FGF21−/− mice with PBS administration than that in wild-type mice and FGF21−/− mice with FGF21 administration. Arrows: TTC-positive (red) myocardium within the area at risk. Scale: 1 mm. (D) Graphic representation of the influence of FGF21 on the fraction of acute myocardial infarcts in reference to the area at risk. Means and SDs are presented (n = 8). The P value was estimated by ANOVA among all groups. The post-hoc pairwise multiple comparisons P values are presented in Supplementary Table 3. (E) AZAN-stained left ventricular sections from wild-type mice and FGF21−/− mice with administration of PBS or recombinant FGF21 at 5, 10, and 30 days after myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Red: Intact myocardium. Blue: Myocardial infarcts and fibrous tissue. Scale bar: 1 mm. (F) Graphic representation of the fraction of myocardial infarcts in wild-type mice (blue) and FGF21−/− mice with administration of PBS (red) or recombinant FGF21 (purple) at 5, 10, and 30 days after myocardial injury. Means and SDs are presented (n = 6). The P value was estimated by ANOVA and is <0.0001 for both time- and treatment-based comparisons. The post-hoc pairwise multiple comparisons P values are presented in Supplementary Table 4.