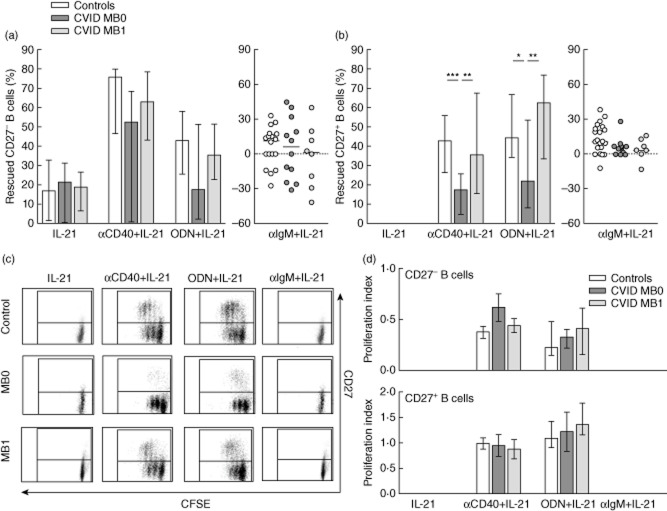
Fig. 5.
Interleukin (IL)-21 effect on apoptosis rescue and proliferation of activated peripheral CD27– and CD27+ B cells from common variable immunodeficiency (CVID) patients. (a) Percentage of rescued CD27– and (b) CD27+ B cells upon stimulation with IL-21 alone or in combination with anti-CD40, cytosine–phosphate–guanosine oligodeoxynucleotides (CpG-ODN) or anti-immunoglobulin (Ig)M in healthy controls (n = 22; white bars/dots), CVID MB0 patients (n = 12; dark grey bars/dots) and CVID MB1 patients (n = 8; light grey bars/dots). (c) Representative dot-plots of dividing and non-dividing CD19+CD27–carboxyfluorescein succinimidyl ester (CFSE)+ (lower quadrants) and CD19+CD27+CFSE+ (upper quadrants) B cells from a healthy control (upper row), one CVID MB0 (middle row) and one MB1 (lower row) patient, after stimulation with IL-21 alone or in combination with anti-CD40, CpG-ODN or anti-IgM. (d) Proliferation index of CFSE-labelled CD27– (upper panel) and CD27+ (lower panel) B cells from healthy controls (n = 19; white bars), CVID MB0 (n = 8; dark grey bars) and MB1 (n = 6; light grey bars) patients after stimulation with IL-21 alone or in combination with anti-CD40, CpG-ODN or anti-IgM. No proliferation was detected with IL-21 and anti-IgM + IL-21. Data are given as median and 25th to 75th percentiles (Kruskal–Wallis test P-values: P < 0·05*; P < 0·01**; P < 0·001***).