Fig. 6.
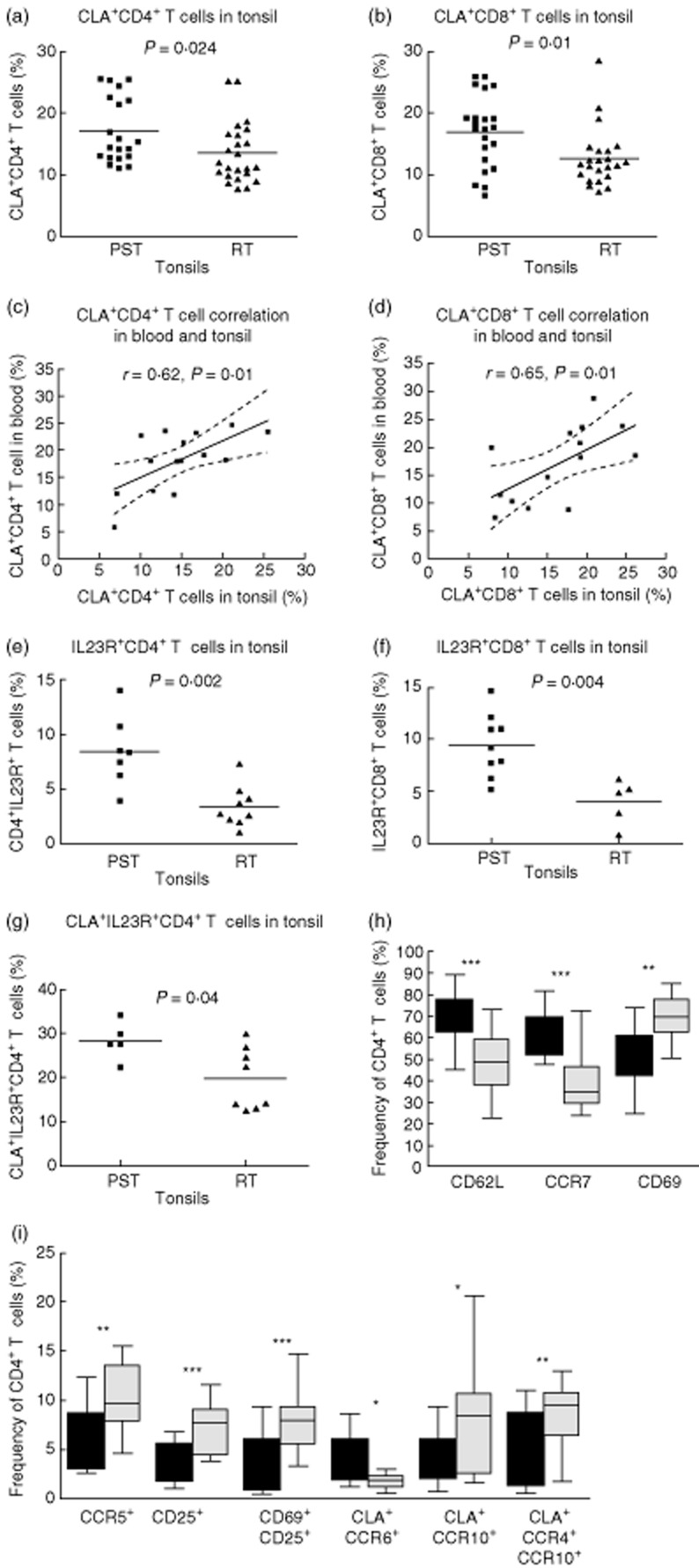
The frequency of skin-homing [cutaneous lymphocyte-associated antigen (CLA)+] T cells is higher in the psoriasis tonsils (PST) patients, and these cells express interleukin (IL)-23R preferentially. The frequency of CD4+ (P = 0·024) and CD8+ (P = 0·01) T cells expressing CLA was higher in the PST than the control tonsils (a,b). There was a correlation between the frequency of CLA+ T cells in the blood and tonsils of psoriasis patients CD4+ r = 0·62, P = 0·01, CD8+ r = 0·61, P = 0·02 (c,d). PSTs had a higher frequency of CD4+ (P = 0·002) and CD8+ (f, P = 0·004) T cells expressing IL-23R (e,f). Furthermore, the IL-23R was expressed preferentially by CLA+ CD4+ T cells, and such co-expression more frequent in the PST tonsils (g, P = 0·04). The frequency of CD4+ T cells expressing CD69 or CD25 alone (h, P = 0·0002 and i, P = 0·0005) or together (i, P = 0·0005) was higher in the recurrently infected tonsils (RT) tonsils. CCR5 expression was also higher in the RT tonsils (i, P = 0·009). Interestingly, CD69+ CD8+ T cells were more frequent in the RT tonsils (P = 0·03, not shown). Furthermore, CD4+ T cells co-expressing CLA and CCR10 (i, P = 0·047) or CCR4 and CCR10 (i, P = 0·006) were more frequent in the RT tonsils. CD4+ T cells expressing CCR7 (h, P < 0·0001), CD62L (h, P < 0·0001) or CLA and CCR6 (i, P = 0·047) were more frequent in PST than RT tonsils. Dotted lines indicate 95% confidence intervals with Spearman's correlation in (c) and (d). For grouped data, statistical significance was determined using Student's t-test or Mann–Whitney U-test as appropriate. Box-plots show median and 95% confidence intervals for PST (n = 11, filled boxes) and RT (n = 22, grey boxes) tonsils.
