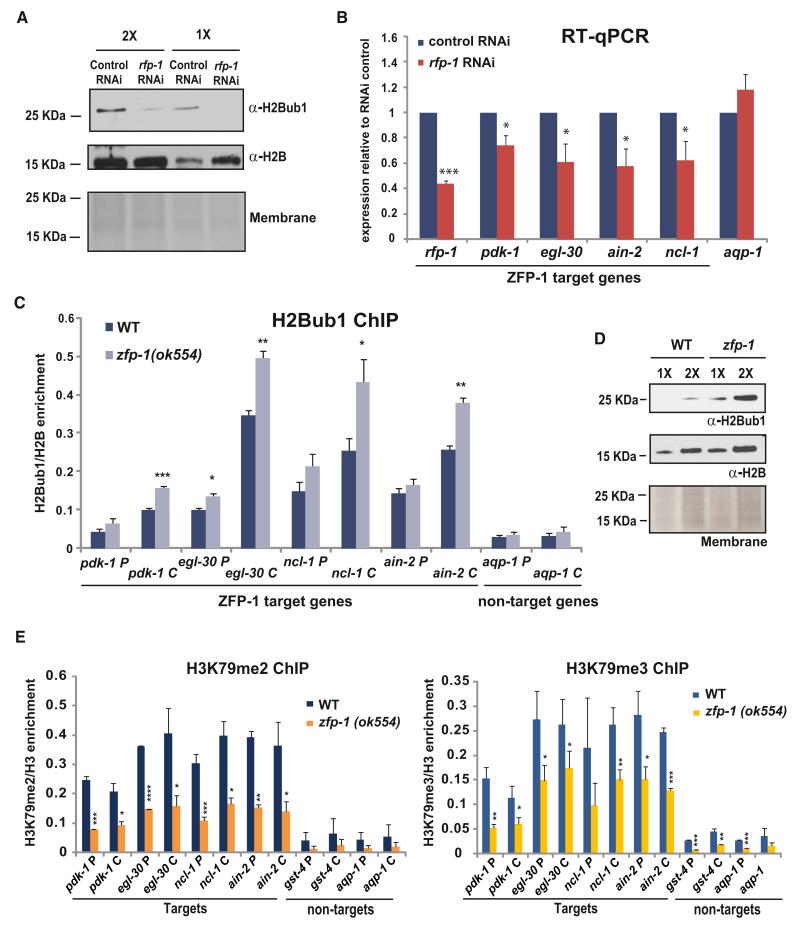
Figure 6. H2B Monoubiqutination Promotes the Transcription of ZFP-1 Target Genes and Is Suppressed by ZFP-1.
(A) Western blot demonstrating that inhibition of C. elegans Bre1 homolog rfp-1 by RNAi leads to a decrease in H2B ubiqutination. Hereafter, H2B western and Ponceau S staining of the membrane are shown as loading controls. (B,C, and E) * indicates a significance of p < 0.05, ** indicates p < 0.01, and *** indicates p < 0.005 in comparison to corresponding controls.
(B) Expression of ZFP-1 target genes is decreased in rfp-1(RNAi) animals as measured by qRT-PCR. act-3 mRNA expression is used as an internal control. The results of two biological replicas are shown. Error bars represent SD.
(C) The level of H2Bub1 is increased on ZFP-1 target genes in the zfp-1(ok554) mutant. The results of two independent ChIP-qPCR experiments are shown. Error bars represent SD.
(D) Western blot demonstrating a global increase in H2Bub1 in zfp-1(ok554).
(E) The level of H3K79me2 and H3K79me3 is decreased on ZFP-1 target genes in the zfp-1(ok554) mutant. The results of two independent ChIP-qPCR experiments are shown. Error bars represent SD.