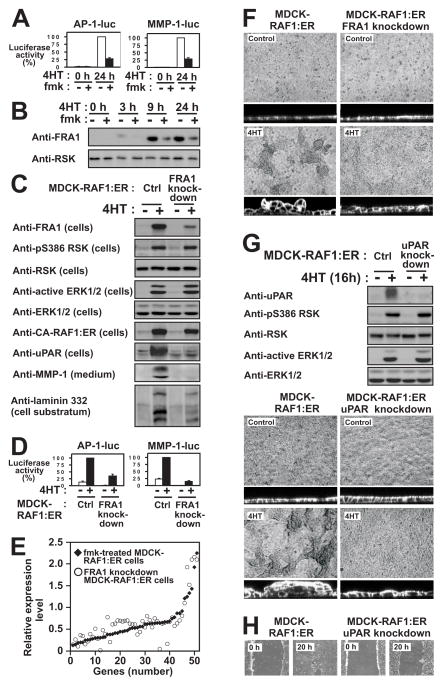
Figure 5. RSK induces the expression of FRA1 to promote induction of pro-motile/invasive genes and phenotypes in MDCK epithelial cells.
(A) MDCK-RAF1:ER cells transfected with AP1-luc or MMP1-luc reporter plasmids were exposed to 1 μM 4HT and 6 μM fmk as indicated, and analysed for reporter gene expression after 24 h.
(B) MDCK-RAF1:ER cells were exposed to 1 μM 4HT and 6 μM fmk as indicated, and analysed by immunoblotting.
(C) MDCK-RAF1:ER cells without (Ctrl) or with knockdown of FRA1 were exposed to 1 μM 4HT as indicated, and analysed by immunoblotting after 24 h.
(D) MDCK-RAF1:ER cells without (Ctrl) or with knockdown of FRA1 were transfected with AP1-luc or MMP1-luc reporter plasmids and analysed as described in (B).
(E) Graphical representation illustrating that the 53 fmk-sensitive genes that were also sensitive to FRA1 knockdown, quantitatively shows very similar sensitivity. Dot and diamond located at the same position of the X axis represent the same gene.
(F) MDCK-RAF1:ER cells with or without knockdown of FRA1 were exposed or not to 1 μM 4HT as indicated, and assessed for multilayering after 24 h, as described in legend to Fig. 2A.
(G) MDCK-RAF1:ER cells without (Ctrl) or with uPAR knockdown were treated and analyzed as described in (C).
(H) Wound healing assays on MDCK-RAF1:ER cells without (Ctrl) or with uPAR knockdown were performed as described in Fig. 2B.
Experiments were conducted 3–4 times with similar results. Data in (A) and (D) are mean ±SD of 3 independent experiments.