Fig. 2. HLA-C expression level correlates with frequency of viral escape mutation and HIV-specific CTL responses.
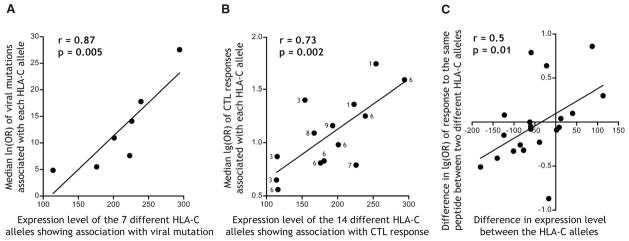
(A) Analysis of viral sequences from 1888 Clade B–infected individuals revealed 12 epitopes containing viral mutations that were associated independently with an HLA-C allele. Median ln(OR) for associations with each of the seven different HLA-C alleles involved correlated positively with the expression level of these alleles. (B) Clade C–infected Africans (n = 1010) were screened for CTL responses to overlapping peptides spanning the HIV proteome, and median log OR of all responses independently associated with each HLA-C allele are plotted. The number of peptide responses associated with each HLA-C allele is labeled next to each point (total number of CTL responses is 71). At least one HLA-C–restricted CTL response was detected in 71% of individuals in the population. (C) Differences in the odds of detecting a response to the same peptide when restricted by different HLA-C alleles correlate with the difference in expression level of these allelic pairs. Pearson coefficients are reported for each correlation.
