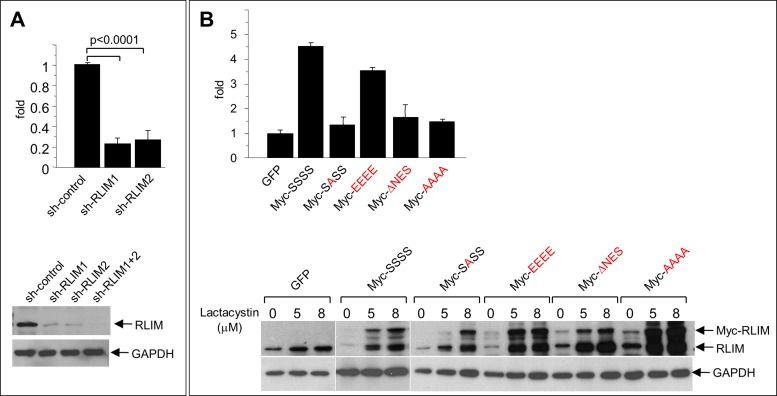
FIGURE 6:
Shuttling of RLIM is important for its function of promoting cell motility. (A) Knockdown of RLIM inhibits cell motility. MCF7 cells were infected with lentivirus containing control or short hairpin RNA against RLIM. Top, motility of infected MCF7 cells as measured in Transwell migration assays. Averages ± SEM for five independent measurements. Bottom, representative Western blot of infected cell extracts. The same blot was hybridized with antibodies against RLIM and GAPDH. (B) Function of RLIM to promote cell motility is dependent on nucleocytoplasmic shuttling. MCF7 cells were infected with lentivirus containing RLIM, various RLIM-NLS mutants, and, as control, GFP. Top, motility of infected MCF7 cells as measured in Transwell migration assays. Averages ± SEM for four independent measurements. Note that overexpression of Myc-RLIM wild type but not shuttling-deficient Myc-RLIM mutant proteins promotes cell migration. Bottom, representative Western blot of infected cell extracts. To compare cellular levels of endogenous with lentivirus-mediated expression of RLIM, cells were treated with various concentrations of the proteasome inhibitor lactacystin for 6 h. The same blot was hybridized with antibodies against RLIM recognizing exogenous and endogenous protein and GAPDH.