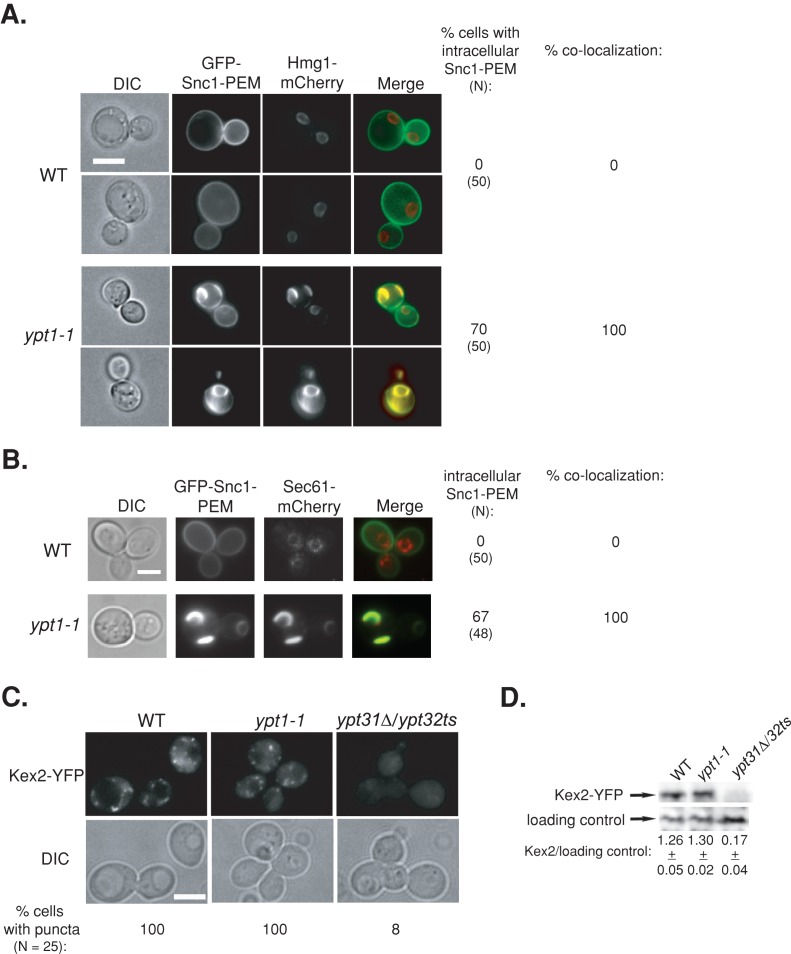
FIGURE 4:
Accumulation of tagged proteins in ypt1-1 mutant cells is not due to an endosome-to-Golgi recycling defect. (A, B) GFP-Snc1-PEM, which cannot be internalized, accumulates in the ER in ypt1-1 mutant cells. Wild-type and ypt1-1 mutant cells expressing Hmg1-mCherry (A) or Sec61-mCherry (B) from their endogenous loci and GFP-Snc1-PEM from a 2 μ plasmid were visualized by live-cell fluorescence microscopy. left to right: DIC, GFP, mCherry, merge, percentage of cells with intracellular GFP-Snc1-PEM (N, number of cells visualized), and percentage colocalization (percentage of cells in which intracellular GFP-Snc1-PEM colocalizes with Hmg1 or Sec61). In wild-type cells all the GFP-Snc1-PEM is on the PM and does not colocalize with the Hmg1 or Sec61 rings. In ypt1-1 mutant cells, intracellular GFP-Snc1-PEM accumulates in ∼70% of the cells and completely colocalizes with Hmg1 and Sec61. (C, D) Endosome-to-Golgi recycling is not defective in ypt1-1 mutant cells. Endogenous Kex2-YFP was expressed in wild-type and ypt1-1 and ypt31∆/32ts mutant cells. Cells were visualized by live-cell fluorescence microscopy (C). Left to right, DIC, YFP, and percentage of cells with GFP puncta (N, number of cells visualized). Lysates from wild-type and ypt1-1 and ypt31∆/32ts mutant cells expressing Kex2-YFP were subjected to immunoblot analysis using anti-GFP antibodies (D). Bands were quantified, and the ratio of Kex2 over the loading control is shown; ±, SD. In wild-type and ypt1-1 mutant cells, the level of Kex2-YFP is similar, and Kex2-YFP puncta were observed. In contrast, in ypt31∆/32ts mutant cells, which are defective in endosome-to-Golgi transport, the level of Kex2-YFP is significantly lower, and almost no Kex2-YFP puncta were seen. Bar, 5 μm. Results represent at least two independent experiments.