Figure 3. siRNA mediated knock-down of C/EBPβ or NF-κB/RelA attenuates the pro-inflammatory cytokine induction of HSD11B1.
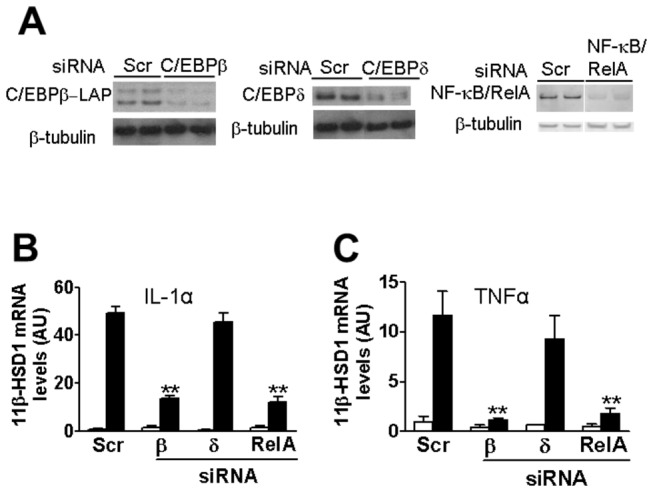
(A) Representative western blots (12.5µg protein/lane) showing levels of C/EBPβ (left panel), C/EBPδ (middle panel) and NF-κB/RelA (right panel) 24h after transfection of cells with scrambled RNA (Scr; as control) or siRNAs targeting C/EBPβ, C/EBPδ or NF-κB/RelA. Blots were stripped and reprobed with β-tubulin antibody, as loading control. In the C/EBPδ and NF-κB/RelA westerns, all samples were analysed in the same gel but not all in adjacent lanes. (B, C) Real-time PCR measurement of HSD11B1 mRNA in untreated cells (white bars) or cells treated for 24h with IL-1α (B; black bars) or TNFα (C; black bars), 24h after transfection with scrambled RNA (Scr) or siRNA targeting C/EBPβ (β), C/EBPδ (δ) or NF-κB/RelA (RelA). Data are expressed relative to levels in untreated cells transfected with scrambled RNA, arbitrarily set to 1. Values, in arbitrary units (AU), are mean ± SEM; n≥5. **, p<0.001, compared to cells transfected with scrambled RNA followed by IL-1α/TNFα treatment.
