Figure 6. Chromatin immunoprecipitation assays show binding of C/EBPβ, but not of NF-κB/RelA, to the HSD11B1 P2 promoter following IL-1α treatment.
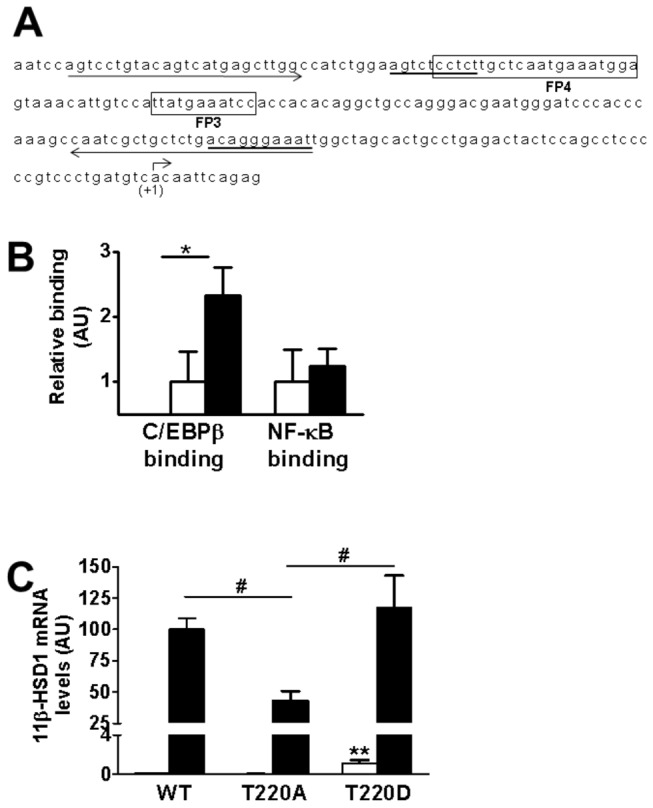
(A) Sequence of the region of the P2 promoter of the HSD11B1 gene that is essential for induction by IL-1α, which includes the previously described C/EBP binding sites, FP3 and FP4 [10] (boxed). The transcription start site (+1) is indicated by a bent arrow. Putative NF-κB binding sites (predicted using AliBaba 2.1 software; Biobase, Biological databases) are underlined. Primers used in ChIP assays are indicated by arrows under the sequence. (B) qPCR quantification of ChIP assays showed C/EBPβ but not NF-κB binding to the P2 promoter of HSD11B1 in cells treated with IL-1α (black bars). White bars, untreated cells. Values, in arbitrary units (AU), are mean ± SEM; n=5. *, p<0.05. (C) qPCR measurements of levels of mRNA encoding 11β-HSD1 in untreated (white bars) or following IL-1α treatment (black bars) of A549 cells transiently transfected with plasmids (50ng) encoding wild-type (WT) chicken C/EBPβ or mutants C/EBPβ(T220A) or C/EBPβ(T220D), abolishing or mimicking, respectively, constitutive phosphorylation of T220 (equivalent to T235 in human C/EBPβ). Data, in arbitrary units (AU), are expressed relative to levels in IL-1α-treated cells transfected with WT C/EBPβ, arbitrarily set to 100 and are mean ± SEM; n=6. **, p<0.001 compared to untreated cells transfected with WT C/EBPβ; #, p<0.05 compared to cells transfected with C/EBPβ(T220A) and treated with IL-1α.
