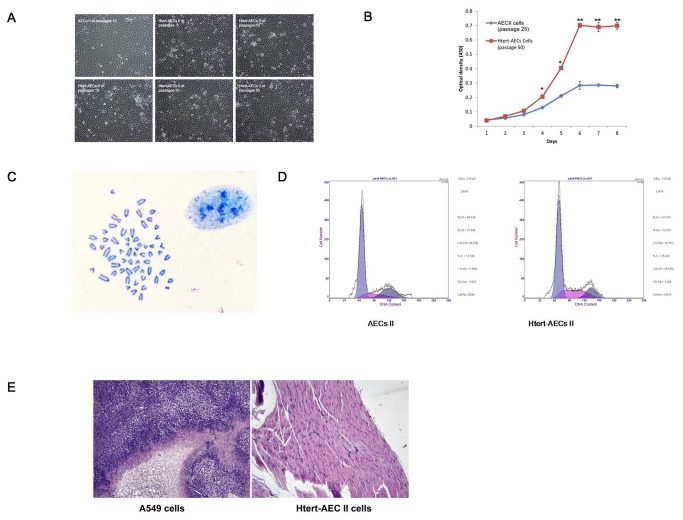
Figure 2. Characteristics of the HTERT-AEC II line at different passages.
A: Cellular morphology of HTERT-AEC II cells at different passages. No obvious morphological differences in HTERT-AEC II cells at different passages were observed compared with normal AEC II cells. B: Cell proliferation abilities of HTERT-AEC II cells at passage 50 and normal AEC II cells at passage 25. C: Karyotype analysis of HTERT-AEC II cells at passage 50. The cell line displays the normal karyotype for cattle. D: Cell cycle comparison between primary AEC II cells at passage 5 and HTERT-AEC II cells at passage 50. E: Tumorigenicity of HTERT-AEC II cells at passage 50. Cells were injected subcutaneously into nude mice. After 2 mo, the three nude mice inoculated with A549 cells rapidly developed tumors. Histologically, tumors evolved into skeletal muscle (left, 100× magnification). However, the three nude mice inoculated with HTERT-AEC II cells did not develop tumors. Histological examination revealed normal tissue structures below the injection site (right, 100× magnification).