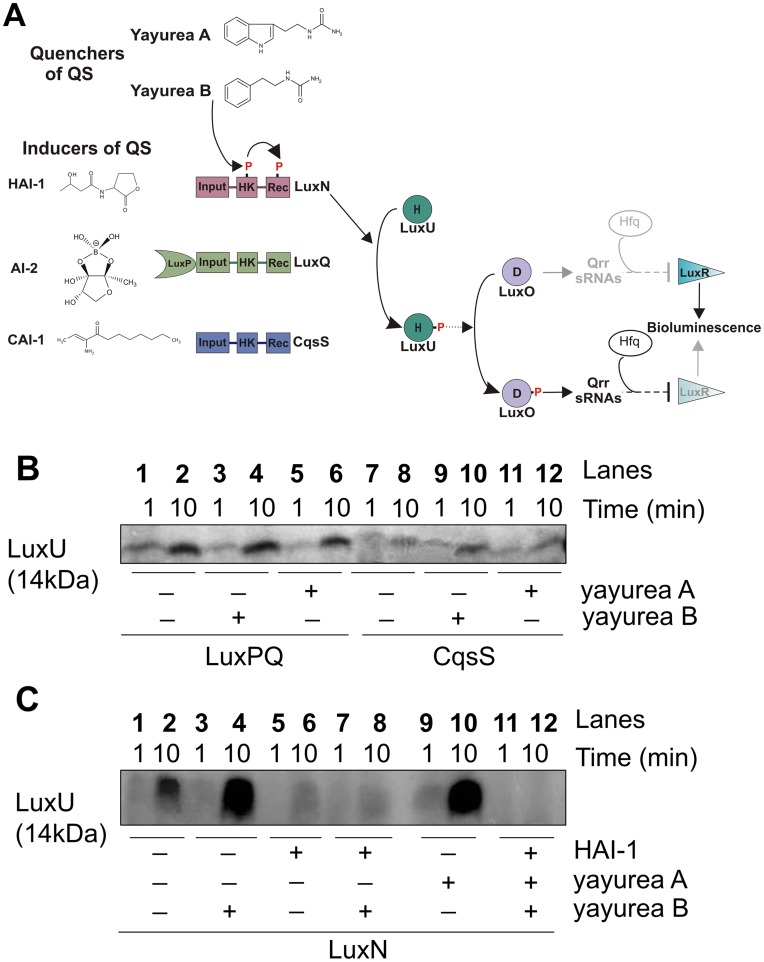
Figure 7. Yayurea A and B are perceived by V. harveyi LuxN receptor.
(A) Schematic representation of the QS phosphorelay in V. harveyi. In the absence of autoinducers (HAI-1, AI-2 and CAI-1) at low cell density, each of the three receptors, LuxN, LuxQ and CqsS, respectively, autophosphorylates at a conserved histidine of their histidine kinase domain (HK). The phosphoryl group is first transferred to the receiver domain (Rec) of the receptor kinase and then to the HPt protein LuxU. LuxP is a periplasmic binding protein. P denotes phosphorylation sites. Upon perception of the autoinducers at high cell density, autophosphorylation of the receptors and the subsequent phosphosphrylation cascade is inhibited. Yayurea A and B stimulated the phosphorylation of the cascade via LuxN. (B) LuxPQ and CqsS mediated phosphorylation of LuxU in the presence of yayurea A and B. (C) LuxN mediated phosphorylation of LuxU in the presence of yayurea A and B and HAI-1. LuxQ, CqsS, LuxN-bearing membrane vesicles and LuxU, were incubated with 100 µM [γ-32P] ATP. The effect of yayurea A, B and HAI-1 (C) on the initial rate of LuxU phosphorylation was evaluated. Each reaction was sampled and stopped at two different time points: after 1 and 10 minutes. Final concentrations were 20 µM for HAI-1, 1.1 mM for yayurea A and 1.3 mM yayurea B, which reflects the in vivo situation. Absence of HAI-1 or yayurea A or B is indicated by “−” and presence by “+”.