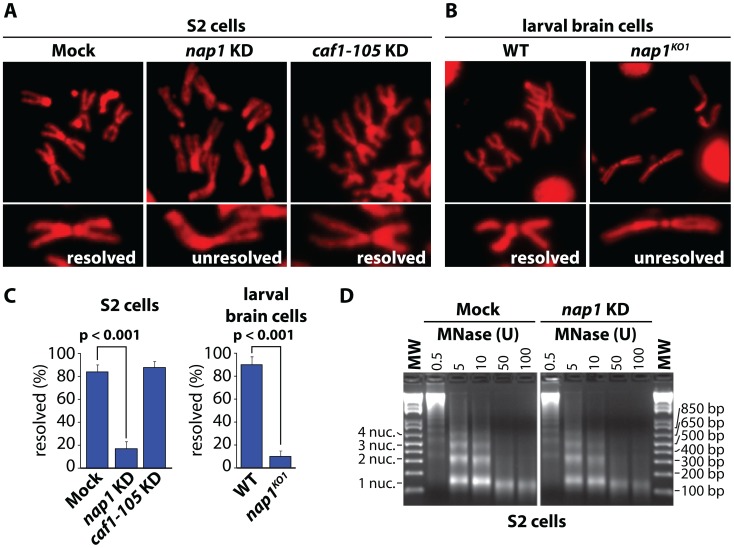
Figure 1. NAP1 is required for sister chromatid resolution.
(A) Analysis of mitotic chromosomes from colchicine-treated S2 cells stained with DAPI (shown in red). Sister chromatids from cells depleted for NAP1 (KD) frequently do not resolve properly, compared to those from mock-treated or CAF1-105 depleted cells. Representative mitotic chromosomes are shown at higher magnification. (B) Mitotic chromosomes from wild type (WT) or nap1KO1 larvae brain cells. (C) Quantification of sister chromatid resolution in the presence or absence of NAP1. The frequency of mitotic cells with resolved sister chromatids is significantly lower in NAP1 depleted cells than in mock-treated or CAF1-105 depleted cells. Likewise, sister chromatid resolution was significantly compromised in brain cells from nap1KO1 compared to wild type larvae. Each analysis was based on >30 cells from 3 biological replicates and significance was determined by a χ2-test. (D) NAP1 knockdown does not affect nucleosome spacing or MNase sensitivity. Formaldehyde cross-linked chromatin prepared from mock-treated or NAP1 depleted S2 cells was digested with indicated units of MNase. Purified DNA was loaded onto a 2% agarose gel and stained with ethidium bromide. DNA fragments corresponding to mono-, di-, tri- and tetranucleosomes are indicated.