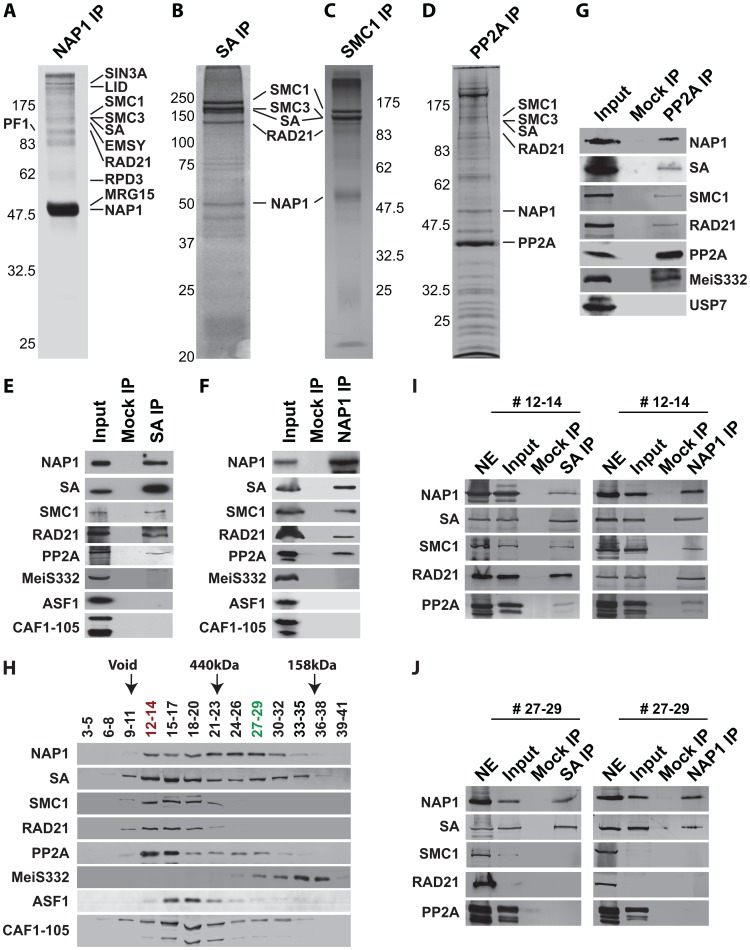
Figure 4. NAP1 interacts biochemically with the core cohesin complex and PP2A.
(A) Proteomic analysis of the NAP1 interaction network. NAP1 and associated proteins were immunopurified from 0–12 hour Drosophila embryo nuclear extracts (NE) using affinity-purified antibodies raised against NAP1. After extensive washes with a buffer containing 600 mM KCl and 0.1% NP40, bound proteins were resolved by SDS-PAGE, visualized by coomassie staining and identified by mass-spectrometry. NAP1, RLAF subunits (SIN3A, LID, EMSY, PF1, RPD3 and MRG15) and cohesin subunits (SMC1/3, SA and RAD21) are indicated. A comprehensive list of identified proteins is provided in Table S1. (B) Identification of SA-associated factors. For a complete list of associated factors see Table S1. (C) Identification of SMC1-associated factors (see Table S1). (D) Identification of PP2A interaction network. Purification of PP2A-associated factors was performed as described above with antibodies against the catalytic subunit. For a list of selected factors associated with PP2A see Table S2. Protein bands corresponding to PP2A catalytic subunit, NAP1 and cohesin subunits, identified by mass spectrometric analysis are indicted. (E) SA was IPed from NE, followed by extensive washes with a buffer containing 600 mM KCl and 0.1% NP40. The binding of NAP1, cohesin subunits, PP2A, MeiS332, and histone chaperones ASF1 and CAF1 was assayed by immunoblotting using the appropriate antibodies. Mock IPs were performed with pre-immune serum. Input represents 10% of the binding reactions. A lack of SA association with MeiS332 was also confirmed under lower stringency (200 mM KCl, 0.1% NP40). (F) Co-IP analysis of NAP1 interactions. Analysis as described above. (G) Co-IP analysis of PP2A interactions. All PP2A interactions were detected under high stringency (600 mM KCl), except for MeiS332, which can be detected only at lower stringency (200 mM KCl). (H) Sephacryl S-300 size-exclusion chromatography analysis of NAP1, cohesin, PP2A and MeiS332. The indicated fractions were resolved by SDS-PAGE followed by immunoblotting. NAP1, PP2A and cohesin subunits SA, SMC1 and RAD21 co-eluted in column fractions corresponding to an apparent molecular mass of ∼1.5 MDa. In addition, NAP1 and SA, but not SMC1 or RAD21, eluted in lower molecular weight fractions of ∼300 kDa. Voided volume (void), determined by Blue Dextran 2000, and elution of the markers ferritin (440 kDa) and aldolase (158 kDa) are indicated. (I) co-IPs of NAP1 and SA from pooled high molecular weight S-300 column fractions (#12–14). IPs were performed as above. Input represents 10% of the binding reactions. (J) co-IPs of NAP1 and SA from pooled lower molecular weight fractions (#27–29). As S-300 fractions #27–29 lack SMC1 and RAD21, NE was used as a control for Western blotting efficiency.