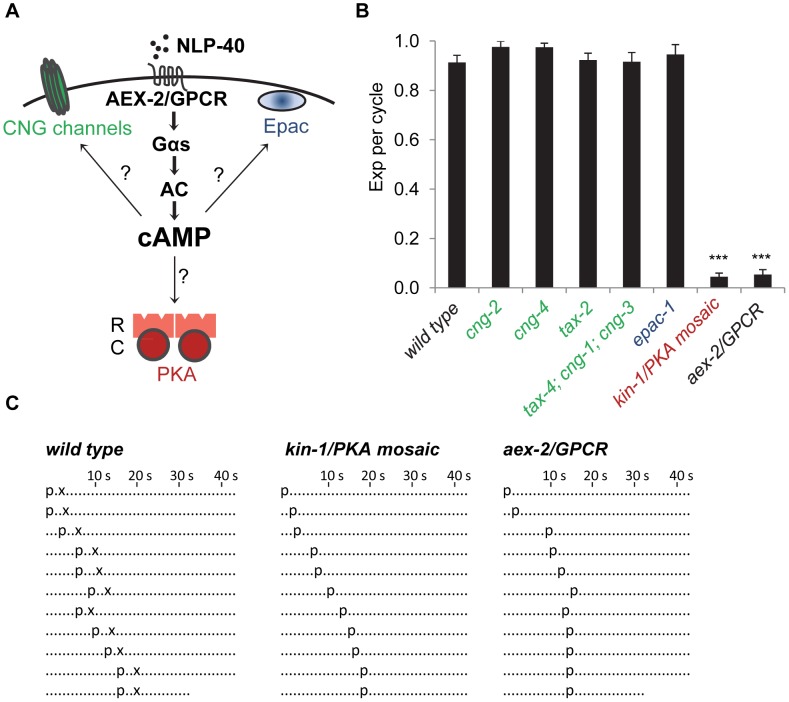
Figure 1. PKA activity is essential for the Exp step.
(A) Diagram of the NLP-40-AEX-2/GPCR peptidergic signaling pathway acting in the GABAergic neurons that controls rhythmic release of GABA during the enteric muscle contraction (Exp) step of the defecation motor program. The potential cAMP targets in this peptidergic pathway are indicated. The PKA holoenzyme is a tetramer with two regulatory subunits (R) and two catalytic subunits (C). (B) Quantification of the Exp step in young adult worms with the indicated genotypes. “Exp per cycle” is defined as the average of the ratio of Exp to pBoc. (C) Representative ethograms of ten consecutive defecation cycles of young adult worms with the indicated genotypes. The kin-1 mosaic represents constipated worms segregated from the strain DG3393: kin-1(ok338) I; tnEx109. Each dot represents 1 s. “p” stands for the pBoc step and “x” indicates the Exp step. aBoc is omitted. Means and standard errors are shown. Asterisks (***) indicate significant difference from wild type: p<0.005 in Student's t-test.