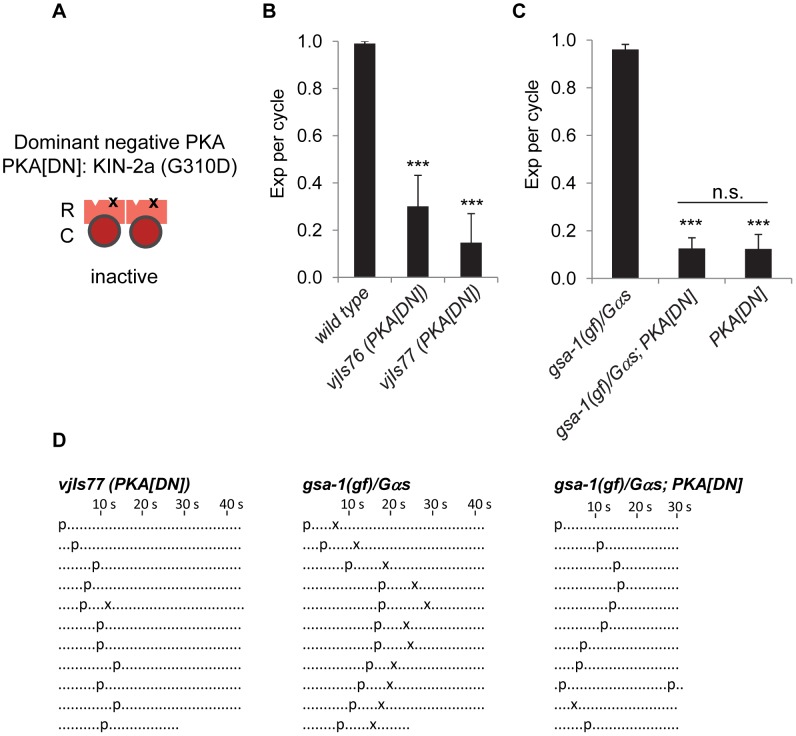
Figure 2. PKA functions in GABAergic neurons to regulate the Exp step.
(A) Diagram showing the construction of dominant negative PKA (PKA[DN]). “R” and “C” indicate the PKA regulatory and catalytic subunit, respectively. “x” represents the substitution (G310D) in the site B of the regulatory subunit KIN-2a, which presumably blocks cAMP binding and prevents its dissociation with PKA catalytic subunit. (B) and (C) Quantification of the Exp step of young adults with the indicated genotypes. PKA[DN] denotes PKA dominant negative transgenic worms (vjIs76 and vjIs77) in which the mutated regulatory subunit kin-2a(G310D) was expressed specifically in GABAergic neurons using unc-47 full length promoter. gsa-1(gf) is a gain-of-function allele (ce81) of gsa-1/Gαs. (D) Representative ethograms of ten consecutive defecation cycles of young adult worms with the indicated genotypes. vjIs77 is used for PKA[DN] in (D). Each dot represents 1 s. “p” stands for the pBoc step and “x” indicates the Exp step. aBoc is omitted. Means and standard errors are shown. Asterisks (***) indicate significant difference from wild type in (B) and gas-1(gf)/Gas in (C): p<0.005 in Student's t-test. “n.s.” indicates no significant difference between indicated groups.