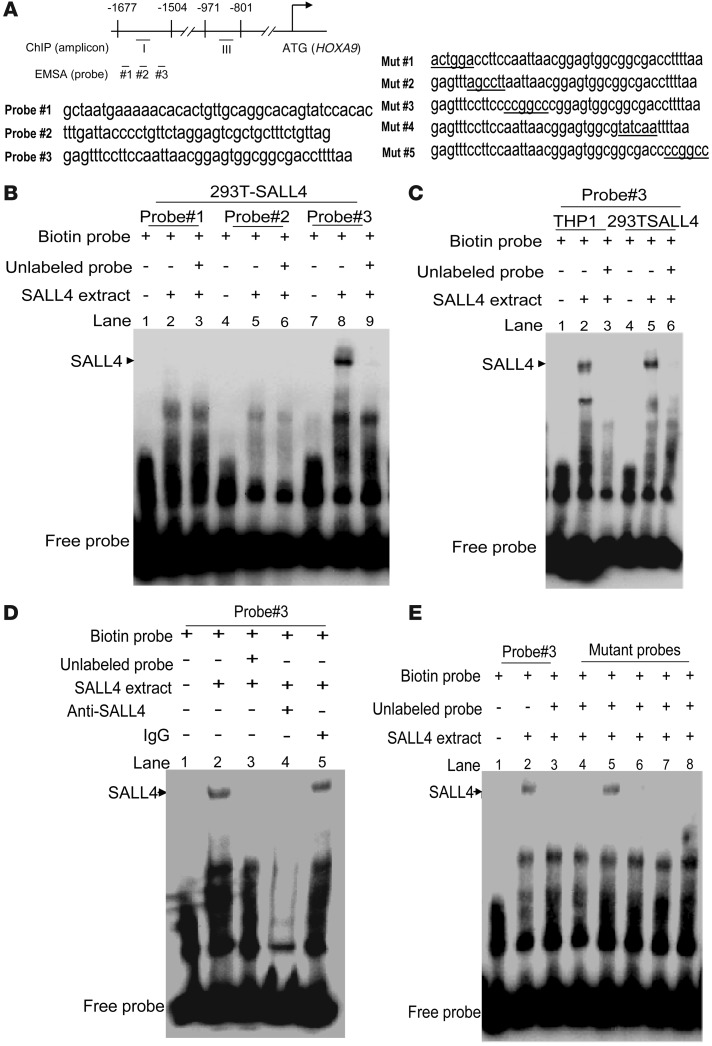
Figure 6. Identification of a SALL4 DNA binding site in the promoter region of HOXA9 by EMSA assays.
(A) Human HOXA9 promoter region. Corresponding locations of amplicons for qPCR and oligo probes for EMSA are indicated. Left: 3 probe sequences. Right: Mutant probe sequences of probe 3. (B) EMSAs were performed to identify the SALL4 DNA binding cells to the HOXA9 promoter region using nuclear extracts from 293T cells transfected with a SALL4 expression construct. Of 3 pairs of oligonucleotide sequences, only probe 3 was specifically bound by SALL4 protein (lane 8); however, this shift could be prevented by competition from 200-fold excess of nonlabeled probe (lane 9). (C) Endogenous SALL4 from THP1 nuclear extracts bound probe 3 specifically (lanes 1–3). Lanes 4–6 show nuclear extracts from 293T-SALL4 as a positive control. (D) SALL4 antibody abolished SALL4 and probe 3 binding (lane 4), but not IgG control antibody (lane 5). (E) Among the 5 mutant probes, only mutant probe 2 (lane 5) failed to inhibit wild-type probe 3 binding to SALL4 protein.