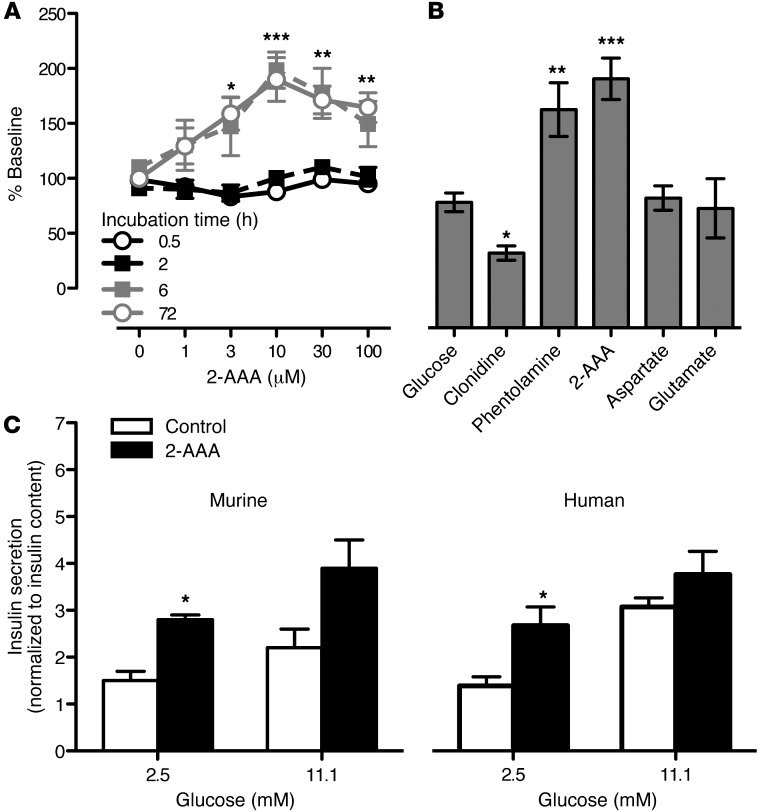
Figure 5. 2-AAA stimulated insulin secretion in BTC6 and islet cell systems.
(A) BTC6 cells were incubated with 2-AAA at concentrations ranging from 0 to 100 μM for 0.5 to 72 hours to assess whether this compound increases insulin secretion in a time and/or dose dependent fashion. (B) We then compared the extent of 2-AAA–stimulated (30 μM) insulin secretion to the effects of clonidine (100 μM) and phentolamine (100 μM), which inhibit and stimulate insulin secretion in islet cells, respectively. Glutamate (30 μM) and aspartate (30 μM) did not elicit insulin secretion over baseline. (C) 2-AAA also augments insulin secretion in primary murine islets and human islets at a basal glucose concentration (2.5 mmol/l). This 2-AAA augmentation effect observed on insulin secretion is reduced in the presence of an insulin stimulatory glucose concentration (11.1 mmol/l). Insulin secretion is normalized to total intracellular insulin content. Data from n = 3 replicates of 15 murine islets or 25 human islets are shown. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.