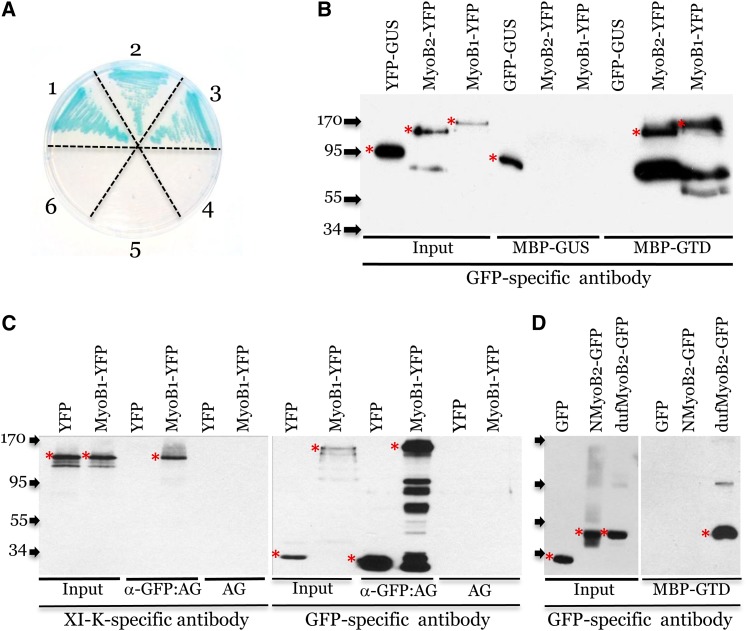
Figure 1.
Interactions between Myosin XI-K and Proteins Encoded by Arabidopsis Genes AT1go88oo (MyoB1), At1g70750 (MyoB2), and At5g16720 (MyoB3).
(A) Y2H assay on SD/-Leu/-Trp/-His/-Ade plates supplemented with X-α-Gal. The combinations of bait and prey proteins used in each sector of the Petri dish were as follows: 1, XI-K-GTD + MyoB1; 2, XI-K-GTD + MyoB2; 3, XI-K-GTD + MyoB3; 4, MyoB3 + GFP; 5, MyoB2 + GFP; 6, MyoB1 + GFP.
(B) Pull-down assay showing specific binding of MyoB1-YFP and MyoB2-YFP to immobilized XI-K GTD (MBP-GTD) but not to immobilized GUS (MBP-GUS). GFP-GUS provides specificity control via binding to MBP-GUS (GUS forms dimers) but not to MBP-GTD.
(C) Coimmunoprecipitation of the MyoB1-YFP–myosin XI-K complexes formed in vivo. α-GFP:AG, GFP-specific monoclonal antibody immobilized on agarose beads; AG, uncharged agarose beads control.
(D) Pull-down assay showing specific binding of the MyoB2 DUF593 domain (dufMyoB2-GFP) to immobilized XI-K GTD (MBP-GTD). Free GFP and N-terminal fragment of MyoB2 (NMyoB2-GFP) provide binding specificity controls. Arrows at the left show protein marker positions with their molecular mass in kilodaltons. Red asterisks mark full-size protein bands; bands of lower molecular mass probably correspond to protein degradation products.