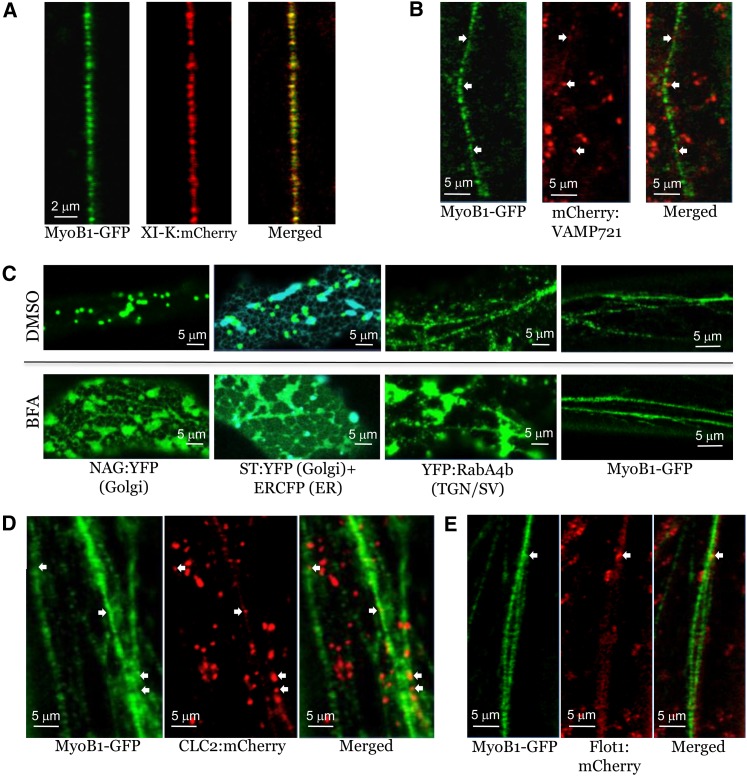
Figure 4.
Analysis of MyoB1-GFP Localization Relative to Distinct Compartment-Specific Markers in the Leaf Epidermal Cells of Transgenic Arabidopsis Plants.
(A) Colocalization of MyoB1-GFP with myosin XI-K:mCherry in myob1 plants.
(B) Colocalization analysis of MyoB1-GFP and exocytic vesicle marker mCherry-VAMP721 in myob1 plants; white arrows indicate positions of a few mCherry-VAMP721–positive bodies that fall into a linear flow of the MyoB1-GFP–positive bodies.
(C) Distribution of Golgi-specific (NAG:YFP and ST:YFP), ER-specific (ERCFP), trans-Golgi network/secretory vesicle (TGN/SV)–specific (YFP:RabA4b) markers in Columbia plants, and MyoB1-GFP in DMSO-treated (control; top row) or BFA-treated (bottom row) leaf epidermal cells of myob1 plants.
(D) Colocalization analysis of MyoB1-GFP and the endocytic vesicle marker CLC2:mCherry in myob1 plants; white arrows indicate a few CLC2:mCherry-positive bodies that fall into the linear flow of the MyoB1-GFP–positive bodies.
(E) Colocalization analysis of MyoB1-GFP and the marker of non-clathrin-coated endocytic vesicles in myob1 plants, Flot1:mCherry; white arrow denotes a Flot1:mCherry-positive body that falls into the linear flow of the MyoB1-GFP–positive bodies.