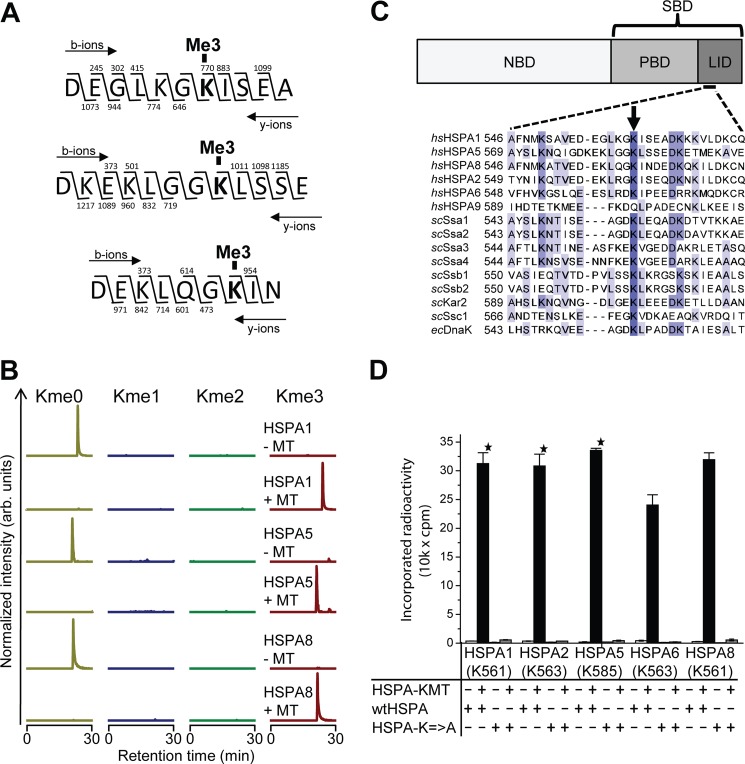
FIGURE 3.
HSPA-KMT trimethylates an evolutionarily conserved lysine in human Hsp70s. A, HSPA-KMT trimethylates HSPA1, HSPA5, and HSPA8. Shown are MS/MS fragmentation patterns of proteolytic trimethylated peptides generated by Asp-N digestion of HSPA-KMT-treated proteins. b- and y-ions supporting trimethylation of HSPA1 Lys-561 (top), HSPA5 Lys-585 (middle), and HSPA8 Lys-561 (bottom) are indicated above and below each peptide sequence, respectively. B, MS chromatograms of Asp-N-generated peptides from Hsp70 proteins incubated with HSPA-KMT. Each chromatogram is gated for the un-, mono-, di-, or trimethylated forms of peptides covering Asp-555–Ala-565 of HSPA1, Asp-578–Glu-589 of HSPA5, or Asp-555–Asn-563 of HSPA8. Samples not treated with HSPA-KMT (MT) are shown as controls. arb., arbitrary. C, HSPA domain organization and protein sequence alignment of selected Hsp70 proteins. Upper panel, schematic representation of Hsp70 domain structure illustrating the N-terminal NBD and the C-terminal substrate-binding domain (SBD), constituted by a β-stranded peptide-binding domain (PBD) and an α-helical lid domain. Lower panel, protein sequence alignment of various Hsp70 proteins from H. sapiens (hs), S. cerevisiae (sc), and E. coli (ec) showing the region surrounding the Lys targeted by HSPA-KMT (arrow). The following proteins are shown: human HSPA1 (P08107), HSPA5 (P11021), HSPA8 (P11142), HSPA2 (P54652), HSPA6 (P17066), and HSPA9 (P38646); S. cerevisiae Ssa1 (P10591), Ssa2 (P10592), Ssa3 (P09435), Ssa4 (P22202), Ssb1 (P11484), Ssb2 (P40150), Kar2 (P16474), and Ssc1 (P0CS90); and E. coli DnaK (P0A6Y8). D, mutational analysis of HSPA-KMT substrates. Wild-type human Hsp70 proteins or mutants (200 pmol) in which the conserved lysine in C had been mutated to alanine were incubated with or without 100 pmol of HSPA-KMT. Error bars indicate S.D. (n = 3) or range of duplicate (star) experiments.