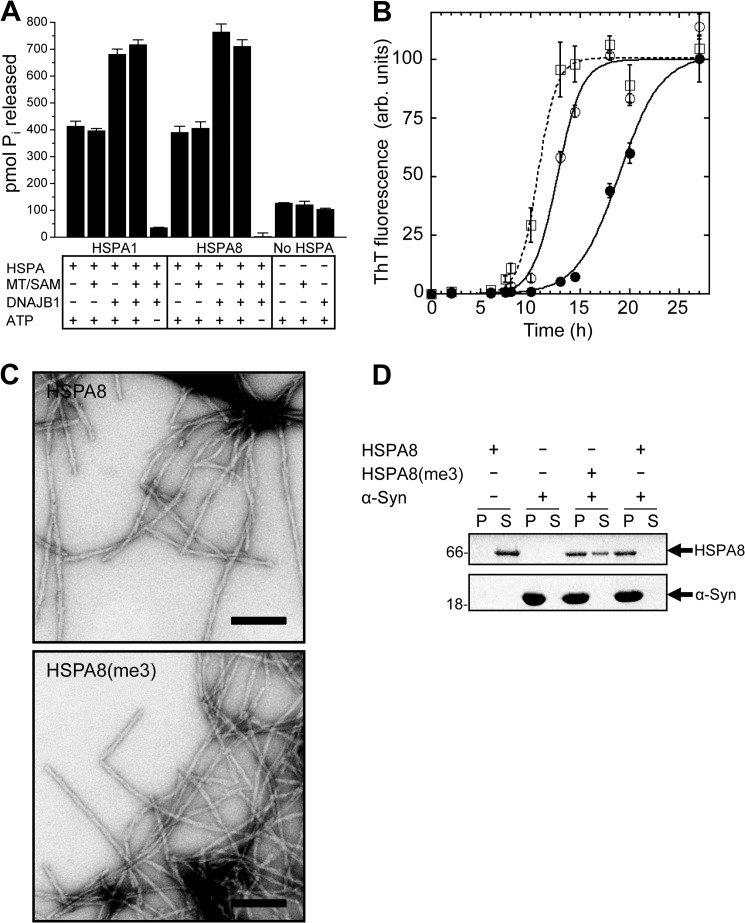
FIGURE 5.
Functional effect of HSPA-KMT-mediated methylation. A, stimulation of basal ATPase activity. Shown is the ATPase activity of HSPA1 and HSPA8 in the absence or presence of DNAJB1 and/or HSPA-KMT (MT) and SAM. ATP and HSPA proteins were omitted in relevant control reactions. ATP hydrolysis was indirectly quantified by the amount of liberated Pi after 1 h at 37 °C. Bars represent the mean, and error bars indicate S.D. (n = 3). B, effect of HSPA-KMT-mediated methylation of HSPA8 on α-Syn assembly. Time courses of α-Syn fibrillation in the absence of HSPA8 (□) or in the presence of unmethylated (●) or Lys-561-trimethylated (○) HSPA8. Data are presented as means ± S.D. (n = 3). A sigmoidal curve (line) was fitted to the experimental data (symbols). ThT, thioflavin T; arb., arbitrary. C, electron micrographs of fibrils formed in the presence of HSPA8 and HSPA8-K561me3 (HSPA8(me3)). Scale bars = 200 nm. D, HSPA-KMT-mediated methylation alters the affinity of HSPA8 for fibrillar α-Syn. Shown are the results from SDS-PAGE analysis of the distribution of HSPA8-K561me3 and HSPA8 in the supernatant (S) and pellet (P) fractions following incubation with preformed fibrillar α-Syn (1 h) and centrifugation at 40,000 × g for 20 min at 20 °C. Control reactions containing only HSPA8 or α-Syn are shown. Molecular mass markers (in kilodaltons) are shown to the left.