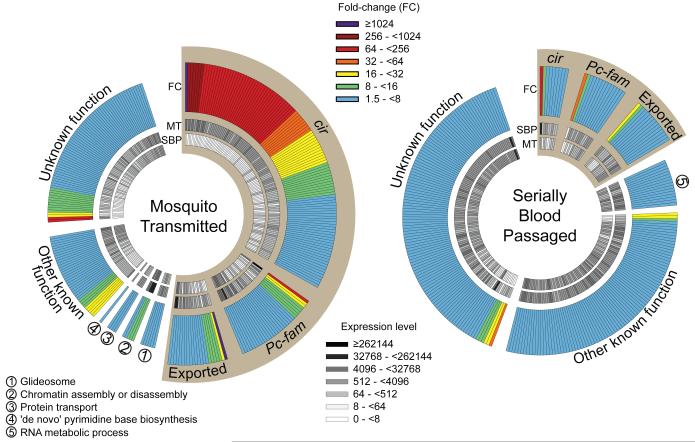
Figure 4.
Mosquito transmission of P.c. chabaudi AS modifies parasite gene expression in the erythrocytic cycle. C57BL/6 mice were injected with 105 SBP Pcc AS or infected with Pcc AS via mosquito bite. Parasites were isolated after 6 cycles of the blood-stage infection, and at the late trophozoite stage of development (98.3% (0.76%) and 97.0% (1.41%) trophozoites for SBP and MT samples, respectively (mean with SD)). Total parasite RNA was extracted and sequenced. Those genes differentially expressed between SBP and MT Pcc AS were determined; genes identified as significantly upregulated in blood-stage parasites following mosquito transmission (left) versus serial blood passage (right) are shown. Each segment represents one gene, and genes are categorised according to the function of their product and ranked based on fold-change (outer circle). The DESeq-normalised expression levels for each gene are also shown (inner circles). Sepia wedges highlight genes whose products are predicted to be exported, or otherwise accessible to the mammalian immune system.