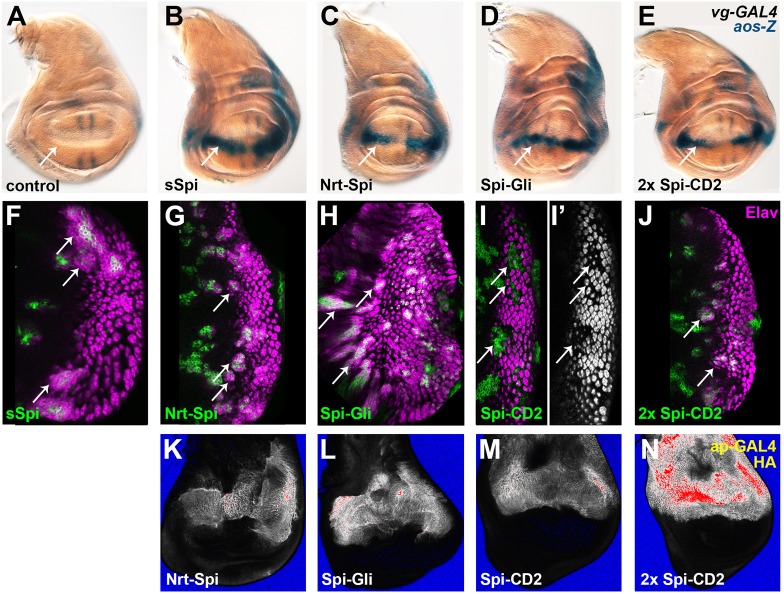
Fig. 2.
Transmembrane Spi chimeras activate the EGFR in vivo. (A–E) Wing imaginal discs expressing sSpi (B), Nrt–Spi (C), Spi–Gli (D) or two copies of Spi–CD2 (E) at the dorsal-ventral midline driven by vg-GAL4 showed ectopic aos-lacZ expression (blue, arrows) compared to control discs (A). (F–J) GFP-marked spi mutant clones (green) expressing sSpi (F), Nrt–Spi (G), Spi–Gli (H) or two copies of Spi–CD2 (J) in eye imaginal discs recruited ectopic photoreceptors (stained with Elav in magenta, arrows). Clones expressing only one copy of Spi–CD2 (I) displayed loss of photoreceptors (arrows; Elav channel shown in white in I′). (K–N) Nrt–Spi (K), Spi–Gli (L) and Spi–CD2 (M) were expressed on the cell surface at similar levels. Expressing two copies of Spi–CD2 (N) resulted in much higher protein levels. Discs were processed in parallel by extracellular immunofluorescent staining with anti-HA antibody (pixel intensity heat map) following expression with apterous-GAL4. Images were taken with identical confocal settings.