Fig. 6.
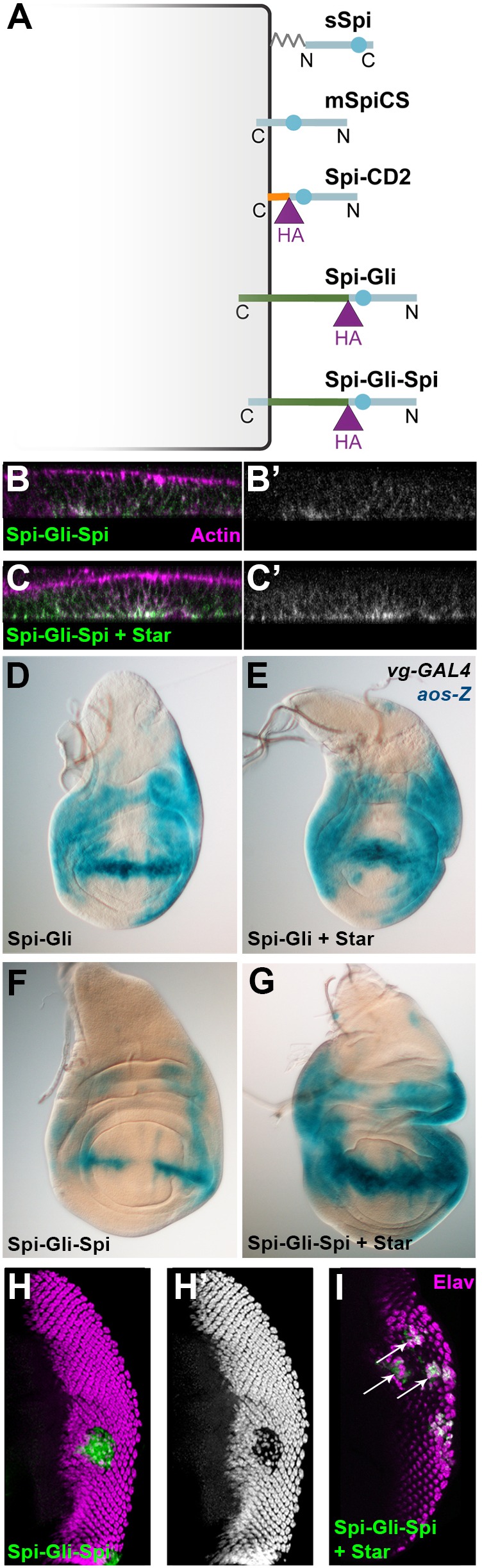
Spi–Gli–Spi activity depends on Star. (A) The Gliotactin cytoplasmic domain in Spi–Gli was replaced with the Spi cytoplasmic domain to generate Spi–Gli–Spi. (B,C) Spi–Gli–Spi, detected with anti-HA extracellular staining (green, white in B′ and C′; TRITC–phalloidin shown in magenta) localized basolaterally in the absence (B) and presence (C) of co-expressed Star, but its cell surface expression was greater when co-expressed with Star. B and C were imaged in parallel with identical confocal settings. (D–G) Both Spi-Gli (D–E) and Spi-Gli-Spi (F–G) induced ectopic aos-lacZ in wing imaginal discs when expressed with vg-GAL4 either alone (D,F) or with co-expressed Star (E,G), but for Spi–Gli–Spi the induction was stronger when it was co-expressed with Star. D–G were stained and imaged in parallel. (H,I) Flip-out clones (green) expressing Spi–Gli–Spi and Star (I) induced ectopic photoreceptor recruitment (marked with Elav in magenta), whereas clones expressing Spi–Gli–Spi without Star caused photoreceptor loss (H, Elav shown alone in H′).
