Fig. 7.
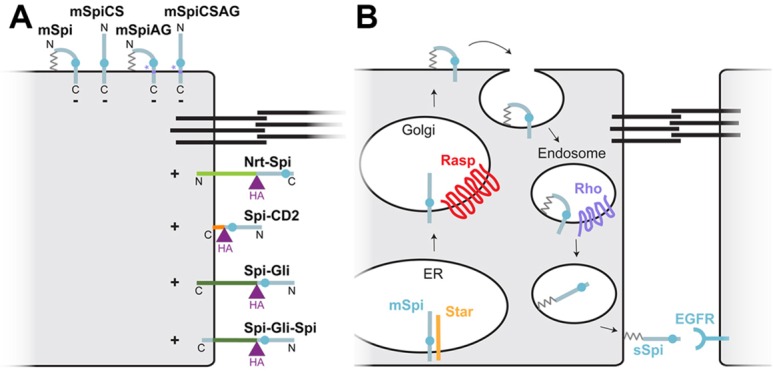
Models for Spi trafficking and activation. (A) Cartoon representing the localization and activity of all the Spi variants tested. Black lines indicate the adherens junctions; mSpi, mSpiCS, mSpiAG and mSpiCSAG localize to the apical surface and are inactive (−), whereas Nrt–Spi, Spi–CD2, Spi–Gli and Spi–Gli–Spi localize to the basolateral surface and are active (+). (B) A model for Spi trafficking. mSpi is exported from the ER with the help of the chaperone protein Star. It is palmitoylated by Rasp in the Golgi and trafficked to the apical cell surface. It might be endocytosed from this location, cleaved in late endosomes by the protease Rho and secreted basolaterally. The palmitate group would tether sSpi to the basolateral plasma membrane.
