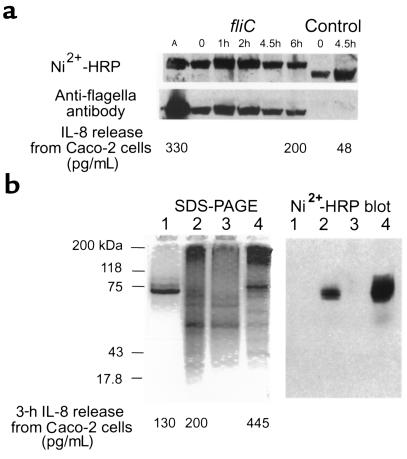
Figure 6.
Expression and purification of FliC-EAEC. (a) BL21(DE3)pLysS transformed with pfliC or pCRT7/NT-E3 (expression control) were harvested from mid–log phase cultures at the indicated times after addition of IPTG. Ten microliters of bacterial lysate was loaded per well for 9% SDS-PAGE, and transferred to PVDF membrane after gel was run. The membrane was probed with Ni2+-HRP to detect polyhistidine-containing proteins, stripped with 0.2 N NaOH, and reprobed with polyclonal anti-flagellar antiserum. A lane containing 2.5 μg of EAEC 042 flagella (A) was included in the gel as a control. For IL-8 release, purified flagella (72 ng) or bacterial lysate (1 μg) was added to 500-μL wells of Caco-2 cells in the same experiment, and supernatant was assayed after 3 hours of incubation. (b) BL21(DE3)pLysS:pfliC was harvested 2 hours after addition of IPTG to mid–log phase culture. Lysates were purified by nickel affinity chromatography, visualized on 9% SDS-PAGE gels, and transferred to a PVDF membrane that was probed with Ni2+-HRP. Lane 1: EAEC 042 flagella, 1.4 μg. Lane 2: Crude lysate, 15 μg. Lane 3: Flow-through from nickel column, 12.5 μg. Lane 4: Eluate from column, 10.8 μg. For IL-8 release, 350 ng of flagella, 1 μg of bacterial lysate, and 1 μg of eluted flagellin were tested.