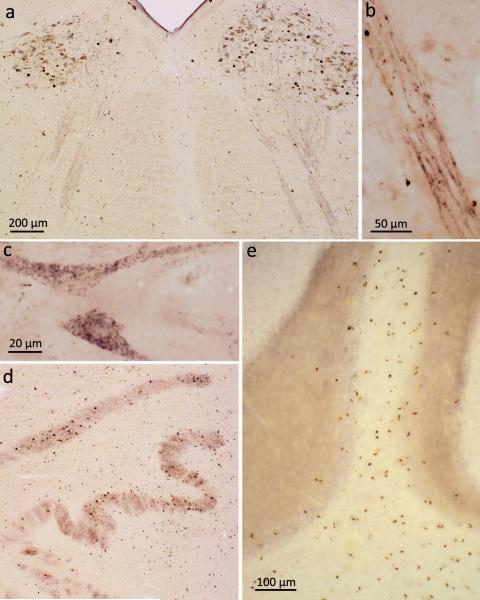
Figure 2. pTDP-43 pathology in bulbar somatomotor nuclei, precerebellar nuclei, and cerebellum.
a. Medulla oblongata section showing extensive ALS-associated pTDP-43 aggregates in neurons of both hypoglossal nuclei (XII) as well as within axons of these cells (case 75, stage 4). b. High resolution micrograph of the intramedullary course of fiber tracts generated from motoneurons of the hypoglossal nucleus. The tract itself contains intraaxonal pTDP-43 aggregates; in addition, immunoreactive oligodendrocytes are located in close proximity to the affected axons (case 75, stage 4). c. Cytoplasmic dash-like pTDP-43 aggregates in motoneurons of the hypoglossal nucleus (case 75, stage 4). d. Section through the medulla oblongata at the level of the hypoglossal nucleus shows involvement of precerebellar nuclei characteristic of stage 2 with extensive pTDP-43 pathology in neurons of the inferior olive. Note the predominant involvement of the superior accessory olivary nucleus and upper lamella of the principal olivary nucleus (case 34, stage 3). e. Section of cerebellar cortex demonstrates multiple pTDP-43-immunopositive oligodendrocytes in cerebellar cortical white matter and deep portions of the cerebellar granular layer (case 10, stage 2). Scale bar in a. is also valid for d. Paraffin-embedded 70 μm sections.