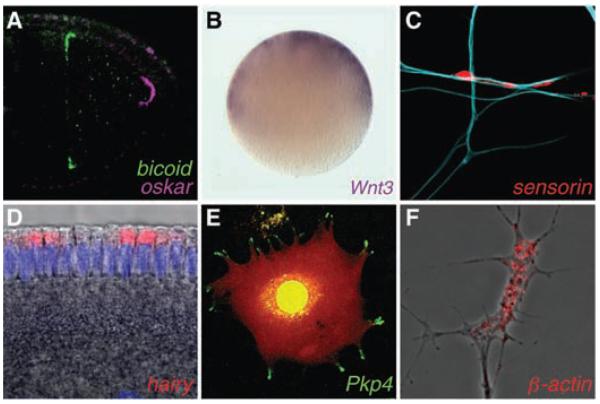
Fig. 2.
Examples of asymmetrically localized mRNAs. (A) Differential localization of mRNA determinants within the Drosophila oocyte. (B) Animal localization of a transcript encoding a signaling molecule required for axis development in the egg of a cnidarian, Clytia. (C) mRNA enrichment in synapses of an Aplysia sensory neuron in response to contact with a target motor neuron (blue). (D) Apical localization of an mRNA in the Drosophila embryo, which facilitates entry of its transcription factor product into the nuclei (purple). (E) mRNA localization in pseudopodial protrusions of a cultured mammalian fibroblast (red signal indicates the cell volume). (F) mRNA enrichment within a Xenopus axonal growth cone. mRNAs were visualized by means of in situ hybridization except in (E), in which the MS2–green fluorescent protein (GFP) system was used. Drosophila images are reproduced from (50) with permission. [Images were kindly provided by (B) T. Momose and E. Houliston, (C) D.O. Wang and K. Martin, (D) M. Dienstbier, (E) S. Mili and I. Macara, and (F) F. van Horck.]