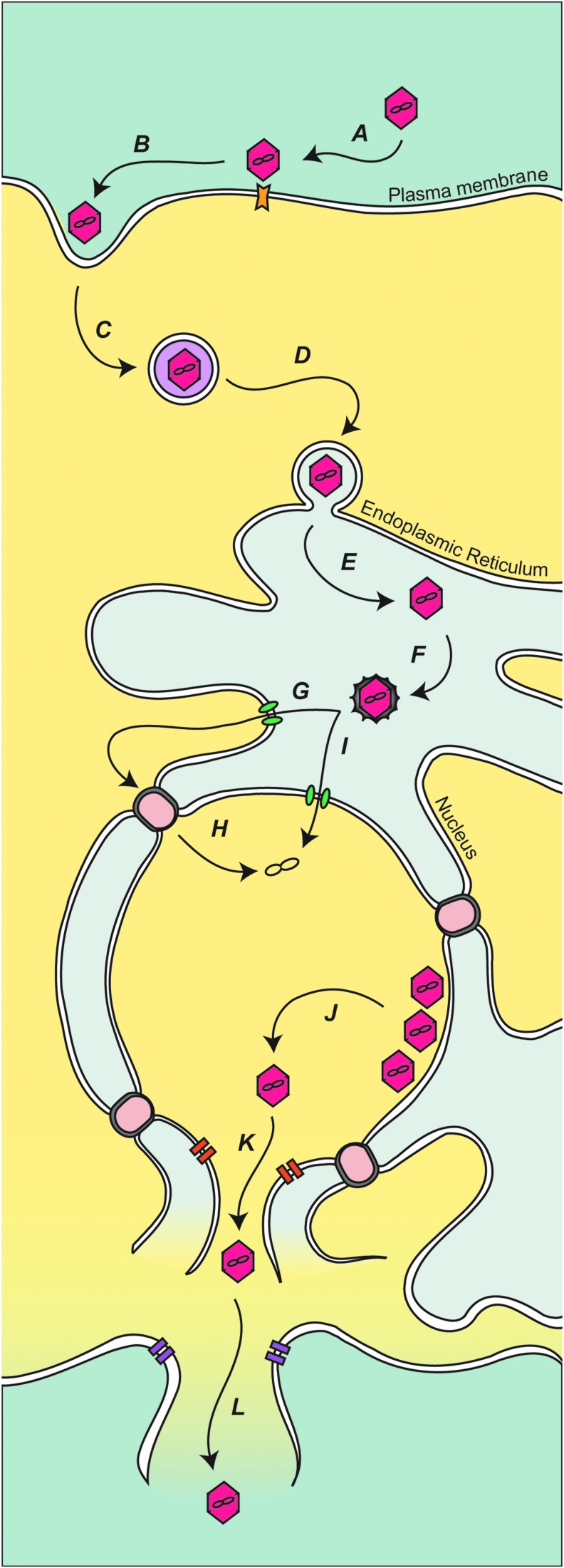
FIG. 2.
Model for polyomavirus infection and release. (A) Polyomavirus is bound at the plasma membrane by cellular receptors. (B) The virus is taken up by invagination of the plasma membrane. (C) The endocytosed virus is transported and (D) delivered to the ER. (E–F) Once the SV40 is in the ER, it is proposed that the viral protein coat is disassembled, releasing or exposing structural proteins VP2 and VP3. The released or exposed coat proteins aid viral transport to either the cytoplasm (G–H) or nucleus (I). (J) Capsid assembly around the viral minichromosome produces virions in the nucleus. (K) Newly produced VP4, along with (L) agnoprotein, triggers cytolysis of the host cell and release of the viral progeny. ER, endoplasmic reticulum.