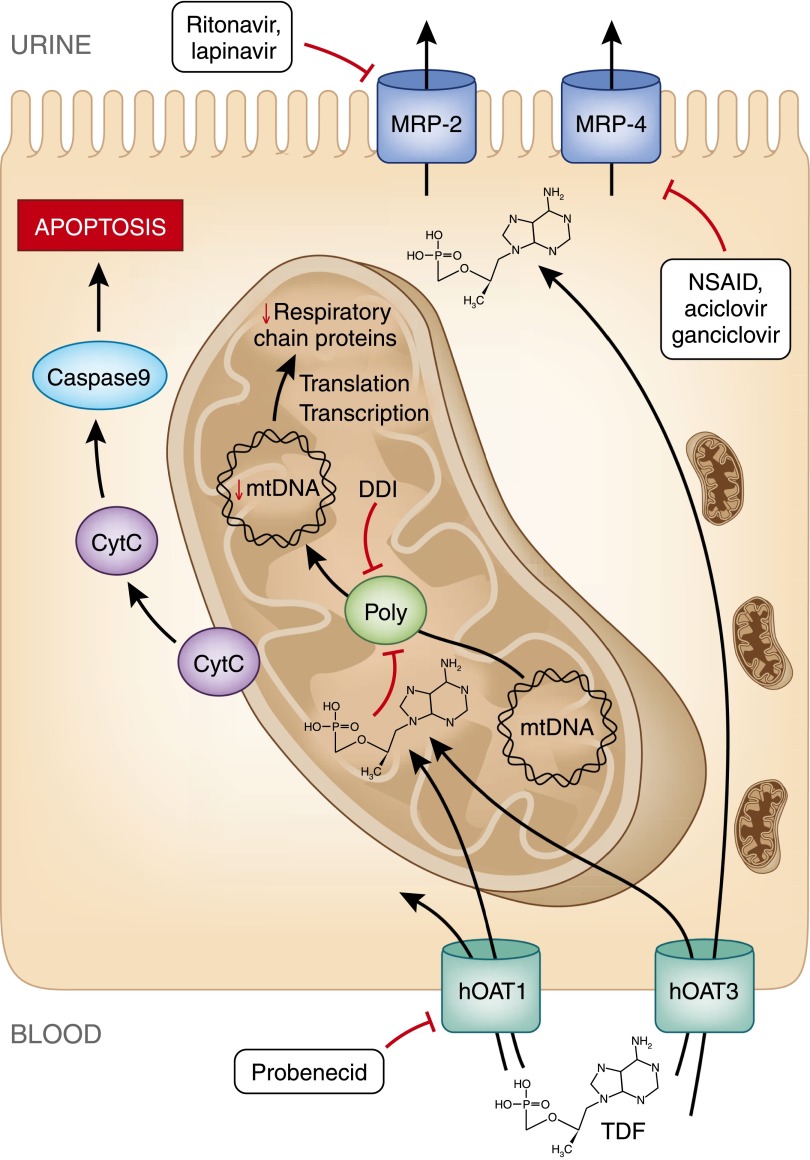
Figure 2.
Cytoplasmic accumulation of TDF is responsible for mDNA depletion and oxidative respiratory chain dysfunction resulting in epithelial cell apoptosis. TDF enters tubular epithelial cells through hOAT1 and hOAT3 receptor at the basolateral pole. It is excreted in tubular lumen through receptors MRP2 and MRP4. TDF intracellular concentrations can be modified by drugs that specifically inhibit these receptors. Once inside a mitochondrion, TDF inhibits DNA polymerase γ, which results in a progressive depletion of mitochondrial DNA, a decreased synthesis of respiratory chain proteins and morphologic abnormalities of mitochondria (enlargement, loss of cristae). Some respiratory chain protein are released in the cytoplasm which can be detected by the caspase pathway and induce apoptosis of the cell. Polγ, DNA polymerase γ; CytC, cytochrome C; NSAID, nonsteroid anti-inflammatory drug.