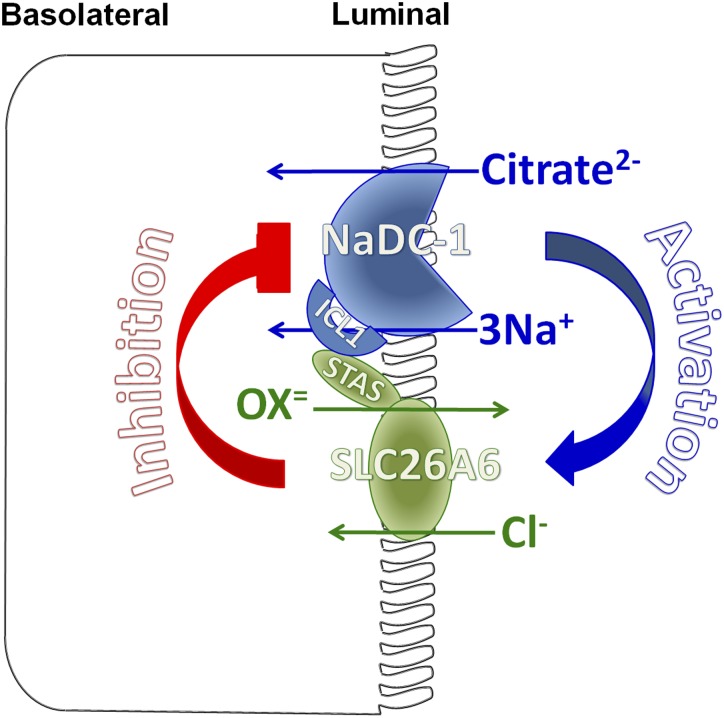
Figure 8.
A model for the molecular mechanism of slc26a6 and NaDC-1 reciprocal regulation in epithelia. The apical slc26a6 and NaDC-1 are present in a complex to allow their interaction. The interaction is mediated by the slc26a6 STAS domain and the NaDC-1 ICL1. When interacting, slc26a6 inhibits NaDC-1, while NaDC-1 activates slc26a6. The result is retention of citrate in the filtrate and perhaps other luminal fluids to chelate part of the Ca2+ to allow safe oxalate excretion. When minimal oxalate excretion is required, the interaction between slc26a6 and NaDC-1 relaxes to increase the activity of NaDC-1 and citrate absorption and salvage. Disruption of this regulation in disease states leads to Ca2+/oxalate stone formation.