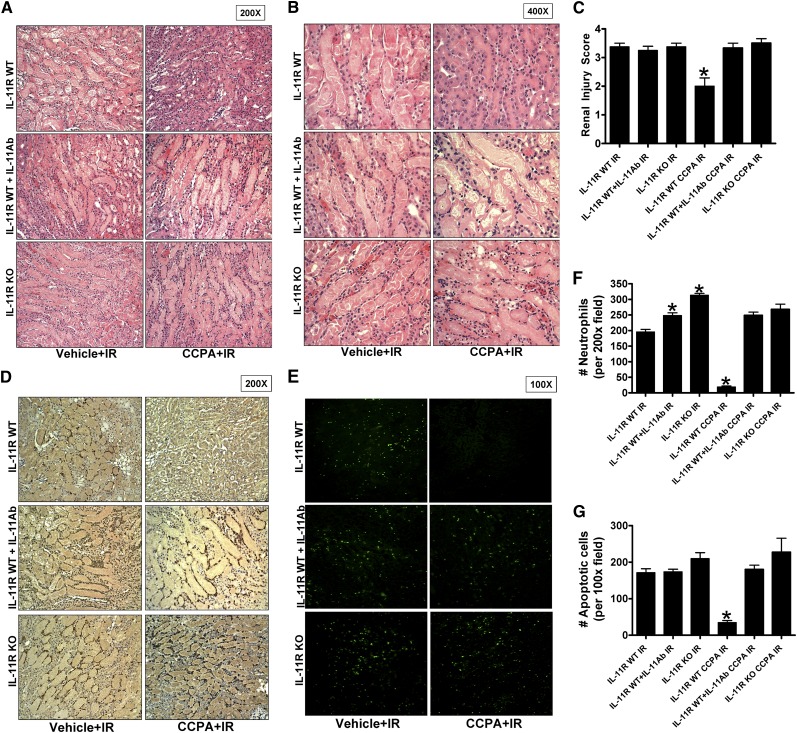
Figure 5.
IL-11 induction is critical for A1AR-mediated reduction in renal tubular necrosis, renal neutrophil infiltration, and renal tubular apoptosis after IR. (A and B) Representative photomicrographs (A: original magnification, ×200; B: original magnification, ×400) hematoxylin and eosin staining of kidney sections of mice subjected to 30 minutes of renal ischemia followed by 24 hours of reperfusion after treatment with a selective A1AR agonist (CCPA, 0.1 mg/kg, intraperitoneally 15 minutes before renal ischemia) or with vehicle. Photographs are representative of 4–5 independent experiments. (C) Summary of Jablonski scale renal injury scores (scale 0–4) for mice subjected to sham operation or renal IR. (D and E) Representative photomicrographs of 4–5 experiments for immunohistochemistry (brown staining) for neutrophil infiltration (D: original magnification, ×200) and TUNEL staining (E, representing apoptotic nuclei: original magnification, ×100) from kidneys of mice subjected to 30 minutes of renal ischemia and 24 hours of reperfusion (IR) after treatment with a selective A1AR agonist (CCPA, 0.1 mg/kg, intraperitoneally 15 minutes before renal ischemia) or with vehicle. Photographs are representative of four independent experiments. (F and G) Quantifications of infiltrated neutrophils per ×200 field (F) and apoptotic cells per ×100 field (G) in the kidneys of mice after renal IR. *P<0.05 versus vehicle-treated mice subjected to renal IR. Error bars represent 1 SEM.