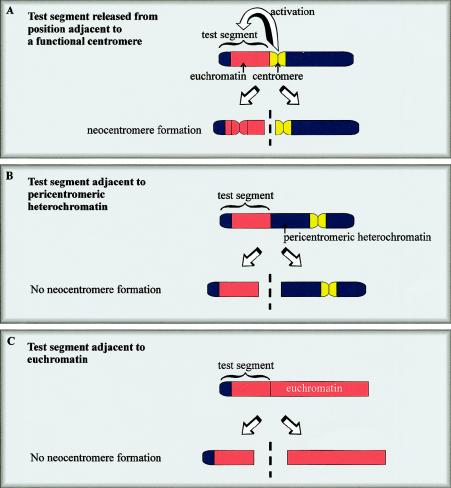
Figure 5.
Generation of neocentromeres in Drosophila. A test segment comprising telomeric heterochromatin and euchromatin forms a functional neocentromere when released from a site immediately adjacent to a normal centromere (A). One model suggests that centromere activity or “centromere imprinting factor” spreads from the existing centromere to the neighboring test DNA, where it activates or imparts a stable centromeric state that can come into independent existence when this DNA is subsequently released. When the same fragment is released from sites adjacent to pericentromeric heterochromatin (B) or euchromatin (C), a neocentromere does not form.