Fig. 2.
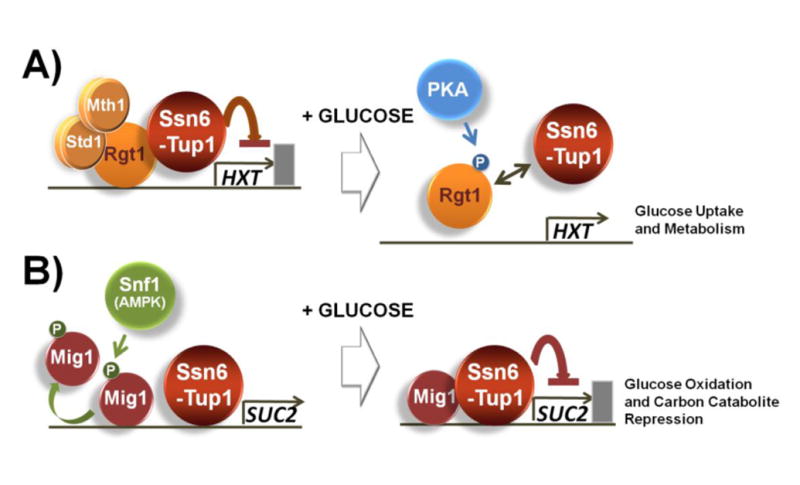
The two glucose responsive repressors Rgt1 and Mig1 are regulated in a similar manner. A) Rgt1 recruits Ssn6-Tup1 in the absence of glucose; however, it is hyperphosphorylated by PKA in the presence of high levels of glucose and dissociated from Ssn6-Tup1, resulting in the induction of expression of genes involved in glucose uptake and metabolism. B) Ssn6-Tup1 interacts with only unphosphorylated Mig1 in high levels of glucose and mediates the repression of genes involved in glucose oxidation and carbon catabolite repression. Snf1-dependent phosphorylation of Mig1 in glucose-limited conditions abolishes interaction with Ssn6-Tup1 [62].
