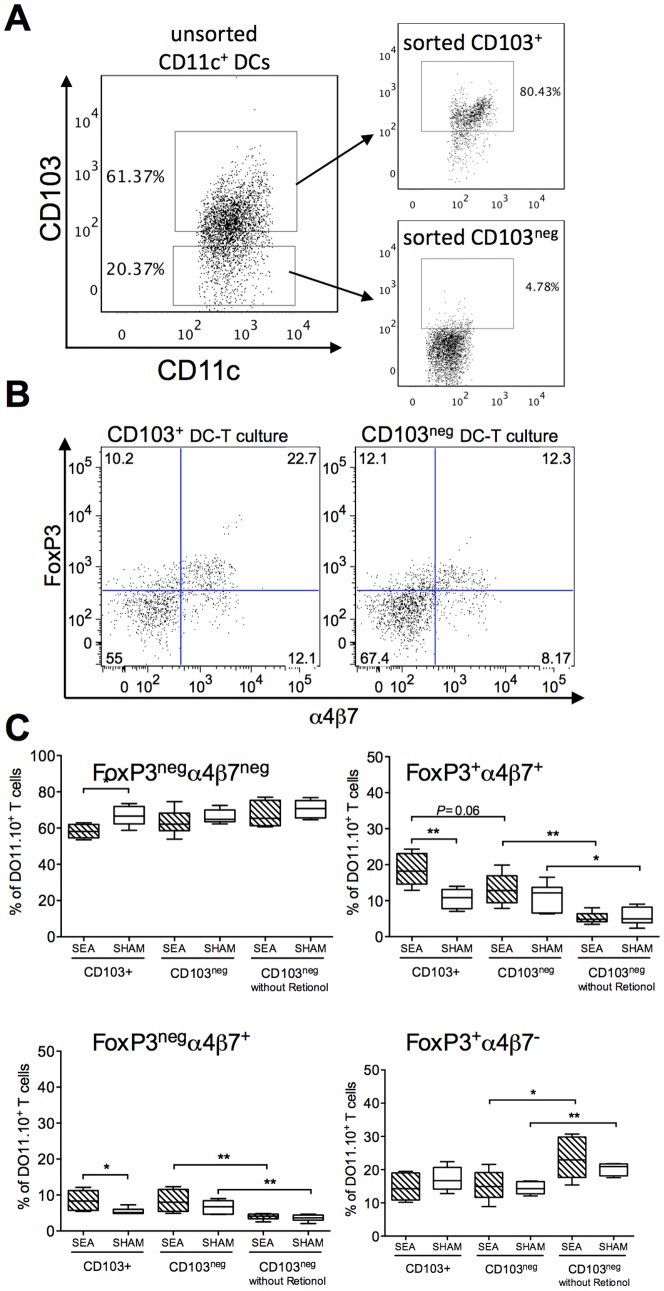
Figure 5. CD103+ DCs from neonatally SEA treated mice exhibit enhanced gut-imprinting and FoxP3-inducing ability in vitro.
Mice (n = 6 in each group) were fed staphylococcal enterotoxin A (SEA) or PBS (SHAM) perorally on six occasions during the first two weeks of life. Mesenteric lymph nodes (MLNs) were collected at four weeks after treatment and CD103+CD11c+and CD103negCD11c+cells were separated by CD11c-positive MACS isolation followed by sorting for CD103+ cells on a flow cytometer. The DCs were pulsed with OVA and co-cultured with OVA-specific DO11.10 CD4+ T cells in medium containing 100 nM retinol. FoxP3 and α4β7 expression was determined in KJ1.26+CD4+ T cells, by flow cytometry, after six days of culture. (A) Representative dot plots of unsorted and CD103-sorted CD11c+ DCs. (B) Representative dot plot and gating strategy of the CD4+KJ1.26+ T cells. C) Proportion of FoxP3neg α4β7neg, FoxP3+ α4β7+, FoxP3neg α4β7+and FoxP3+ α4β7neg cells among the CD4+KJ1.26+ T cells cultivated with CD103+DCs, CD103neg DCs and CD103negDCs in cultures without Retinol. Error bars represent SD and horizontal line shows the median value of the group. Data shown are representative of two independent experiments. * P<0.05, analyzed with Mann-Whitney U-test.