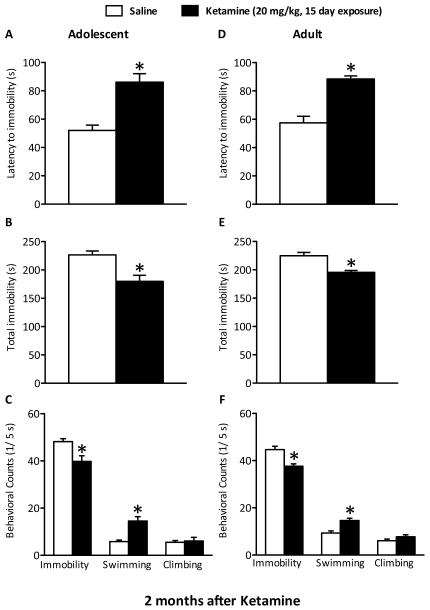
Figure 6.
Lasting effects of repeated (15 days) exposure to ketamine (20 mg/kg, twice daily) on behavioral despair using the forced swim test (FST) paradigm, 2 months after drug exposure, in adolescent (A–C) and adult (D–F) rats. Adolescent (PD35–49; n=12/group) rats show significantly increased latencies to immobility (A), lower total immobility (B), decreased immobility as well as higher swimming counts (C) when compared with saline-treated rats 2 months after drug exposure (p<0.05). Similarly treated adult rats (PD 75–89; n=11–12/group) also exhibited significantly increased latencies to immobility (D), lower total immobility (E), decreased immobility and increased swimming counts (F) 2 months after drug treatment (p<0.05). Data are presented as latencies to become immobile and total immobility (in seconds) and as cumulative 5-second intervals of swimming, climbing, and immobile counts (mean ± SEM). *Significantly different from saline-treated rats (p<0.05).