Fig. 1.
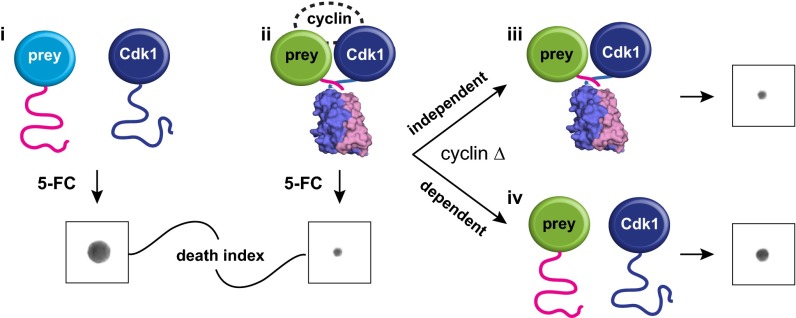
Dissecting Cdk1 complexes using the OyCD PCA. Detecting the interaction between Cdk1 and a protein of interest using the OyCD PCA. Cdk1 and proteins of interest (prey proteins) are fused to OyCD fragments. In the death selection OyCD PCA, (i) the absence of an interaction fails to allow the OyCD reporter enzyme to fold and restore the activity of the native enzyme. Cells expressing these fusion proteins are resistant to 5-FC. (ii) If prey protein interacts with Cdk1, cells are sensitive to 5-FC. When a cyclin gene is deleted (cyclin Δ), (iii) a prey protein can still interact with Cdk1, allowing the reporter fragments to fold; consequently, cells are sensitive to 5-FC. The prey protein–Cdk1 interaction is independent of any cyclin. (iv) If the interaction is cyclin-dependent, the absence of a specific cyclin results in partial or total resistance to 5-FC.