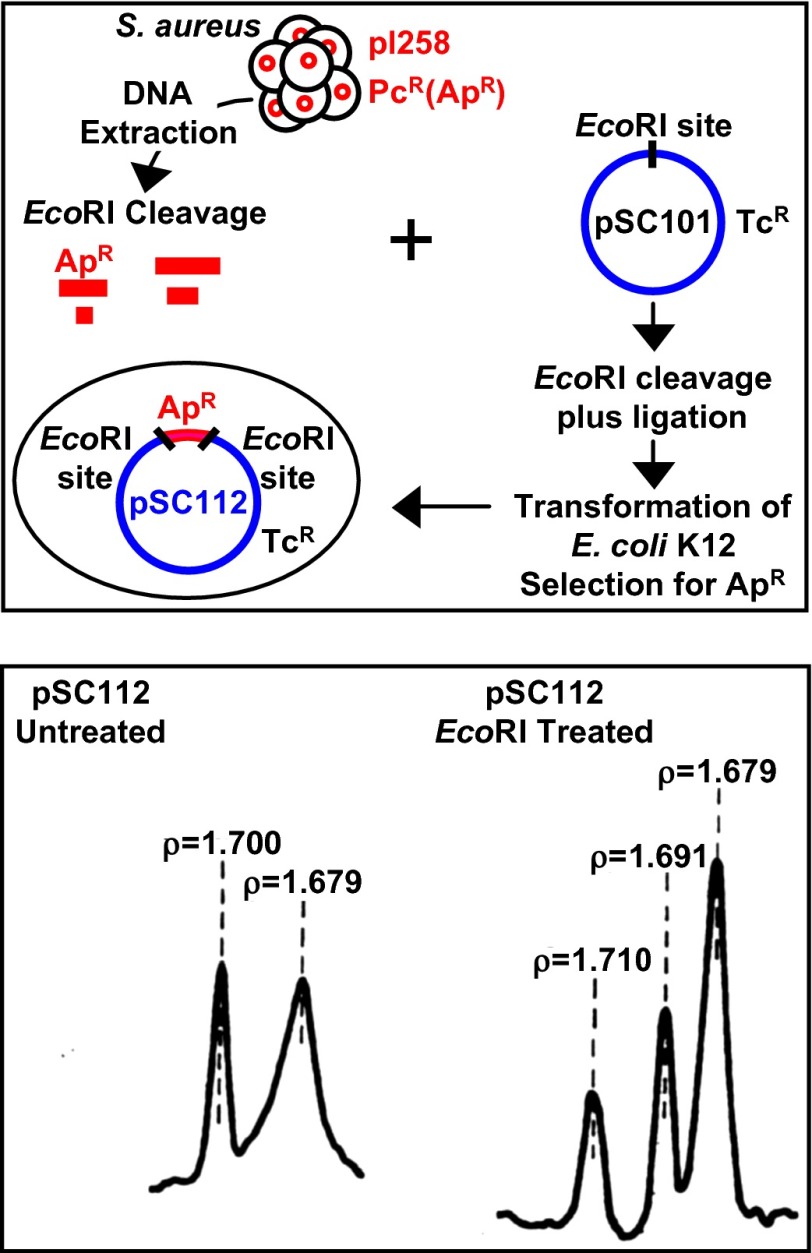
Fig. 4.
Cloning of S. aureus plasmid DNA in E. coli. (Upper) Schematic diagram of strategy used for testing the viability of interspecies DNA hybrids (2). DNA of the pI258 plasmid, which carries a β lactamase gene encoding resistance to penicillins in S. aureus was cleaved by EcoRI endonuclease and mixed with similarly cleaved DNA of the pSC101 vector encoding tetracycline resistance. After ligation, the mixture was introduced into E. coli cells, and colonies that expressed both resistance phenotypes were identified. (Lower) Centrifugation analysis in isopycnic density gradient of plasmid DNA (pSC112) isolated from an E. coli clone expressing both resistances and showing DNA species that band at buoyant densities characteristic of E. coli (ρ = 1.710) and S. aureus (ρ = 1.68–1.69) DNAs and reflect the distinctly different A+T/G+C nucleotide ratios of these unrelated bacterial species. Lower is from ref. 2.