Figure 2.
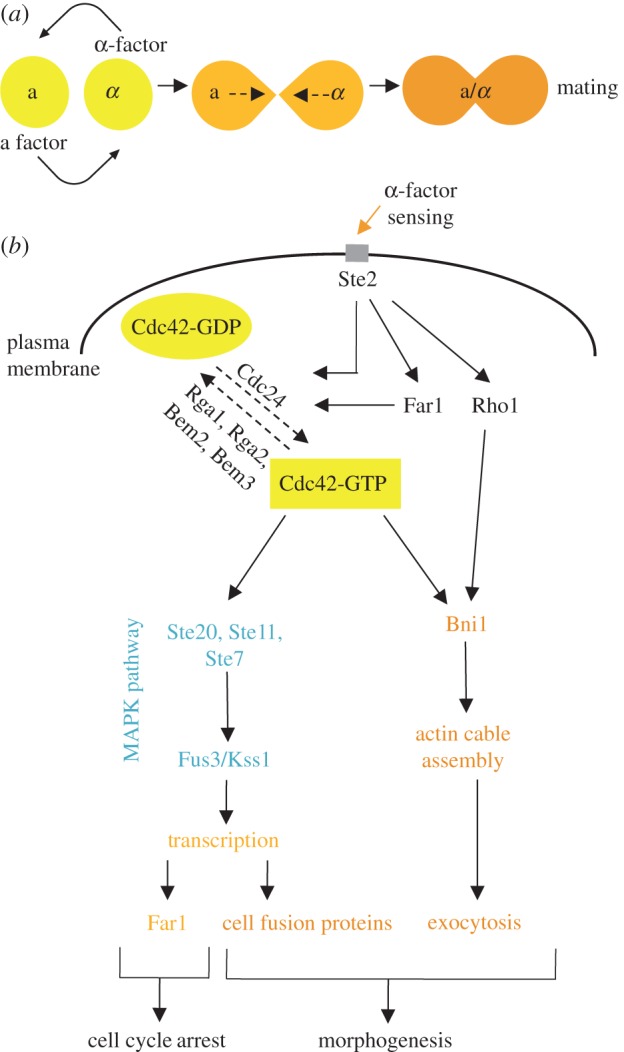
An overview of Cdc42 regulation during mating. (a) Mating begins after exposure to mating pheromone from cells of the opposite mating type, which leads to the outgrowth of a mating projection, or ‘shmoo’. (b) The same Cdc42-based machinery used in budding drives polarized cell growth and shmoo formation during mating. In addition to regulating polarized secretion, Cdc42 also regulates the mating MAPK signalling pathway to turn on mating-specific genes required for cell fusion and the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor Far1, leading to G1 arrest.
