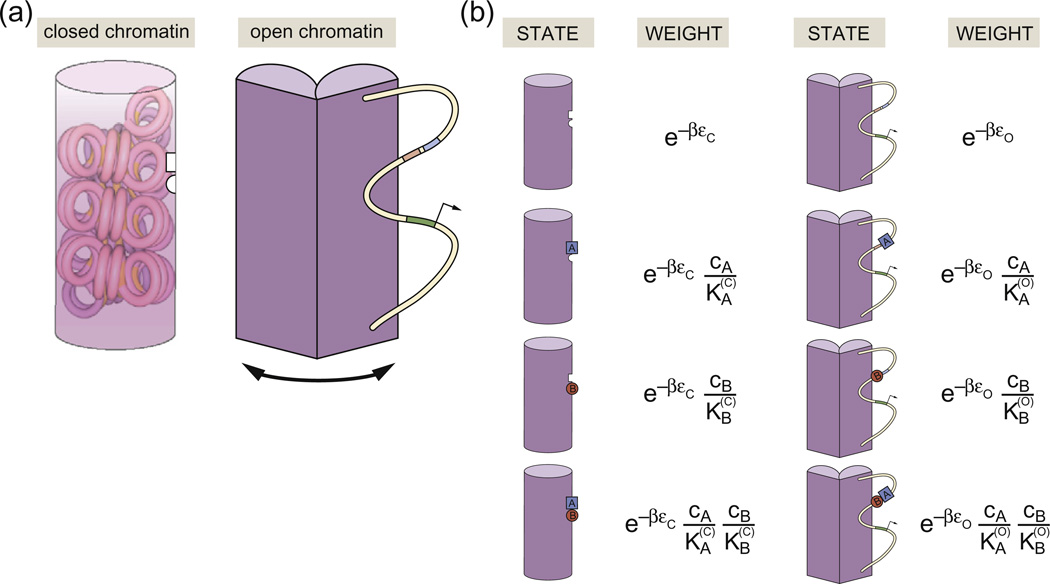
Fig. 7.
Schematic description of MWC chromatin. (a) The genomic DNA exists in two classes of state, one of which is “off” and the other one of which is “on” and permits transcription. Transcription factor binding controls the relative probability of these different eventualities. (b) States and weights for the binding of two transcription factors, here denoted by A and B, which occupy the open and closed conformations with different affinity. The concentration of transcription factors A and B is given by cA and cB, respectively. The conformational energies of the closed and open states are given by εc and εo. The dissociation constant for A is when chromatin is in the closed state and is in the open state, and the dissociation constant for B is when chromatin is in the closed state and is when chromatin is in the open state.