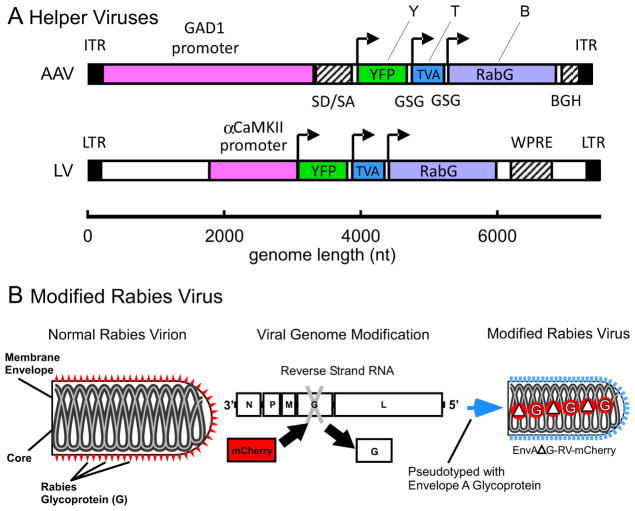
Figure 1. Design of the Cell-Type Specific Vectors and Modified Rabies Virus.
(A) Schematic representation of the transfer vectors for recombinant adeno-associated virus, AAV/GAD1/YTB (top), and lentivirus, LV/αCaMKII/YTB (bottom). Each vector includes a cell-type specific promoter (magenta), GAD1 (glutamic acid decarboxylase 1) or αCaMKII (α-calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II), cis-regulatory sequences (hatched; SD/SA = splice donor and acceptor sequence from human β-globin, BGH = bovine growth hormone polyadenylation signal; WPRE = woodchuck hepatitis virus posttranscriptional regulatory element), and the YTB transgene. YTB codes for three gene products using 2A peptide mediated cleavage [52]: the yellow fluorescent protein reporter (YFP, or Y; yellow), the artificial TVA 950 receptor (TVA, or T; blue), and the glycoprotein from the B-19 strain of rabies (RabG, or B; purple). Arrows indicate the start codons for each gene. Inverted terminal repeats (ITR) and long terminal repeats (LTR) are indicated in black. (B) The rabies virus (RV) has been modified in two ways based on [16]: the glycoprotein gene (G) was deleted (ΔG) and replaced with the gene for mCherry, creating, ΔG-RV-mCherry; and it was subsequently pseudotyped with the envelope A glycoprotein, creating EnvA-ΔG-RV-mCherry.