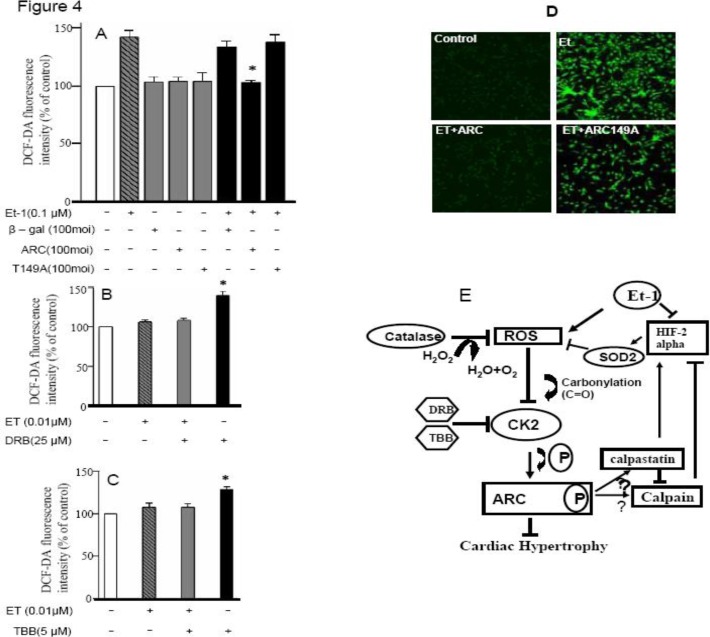
Figure 4.
ARC can control ET 1–induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy by controlling intracellular ROS. A: The cultured neonatal rat cardiomyocytes were infected with adenovirus ARC (AdARC), nonphosphorylated ARC mutant (AdT149 A), or adenovirus-galactosidase construct (Adβ-gal) at the indicated multiplicity of infection (100 moi); 24 hr after infection, they were incubated with 5 μM DCFDA for 30 min at 37oC in the presence of 0.1 μM ET-1. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM of 3 independent experiments. *P <0.05 vs ET-1 + Adβ-gal. B: The cultured neonatal rat cardiomyocytes were incubated with 25 μmol/L DRB; 24 hr after incubation, they were incubated with 5 μM DCFH-DA for 30 min at 37 oC in the presence of 0.01 μM ET-1. Data are expressed as the mean SEM of 3 independent experiments, *P <0.05 vs ET-1. C: 5 μM TBB (50 min incubation)–treated group, *P <0.05 vs ET-1. The data indicate mean ± SEM of 3 independent experiments. D: Representative photographs of control and treated cardiomyocytes from confocal microscope showing fluorescence intensity. E: Hypothetical pathway depicting different events involved during the ARC regulation of ET 1–induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy